 |
 |
- Search
| J Korean Crit Care Nurs > Volume 12(3); 2019 > Article |
|
ABSTRACT
Purpose
The routine evaluation of gastric residuals (RGR) is considered standard care for premature infants. This study evaluated the usefulness of RGR in premature infants.
Methods
The study retrospectively investigated 208 premature infants (gestational aged under 34 weeks) who underwent gavage feeding in a neonatal intensive care unit at a tertiary hospital. The patients were divided into two groups: RGR (n=104) and no-RGR (n=104). Those in the no-RGR group had their gastric residuals checked only if signs of feeding intolerance were present. Clinical outcomes, including the time to reach full enteral feeding (FEF) and the incidences of gastrointestinal disorders such as feeding intolerance (FI) and necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC), were compared. Data were analyzed with SPSS ver. 21, using a Mann-Whitney U test, chi-squared test, and FisherŌĆÖs exact test.
ļ»ĖņłÖņĢäļŖö ņ×ÉĻČü ļé┤ ņä▒ņןĻ│╝ ņ£Āņé¼ĒĢ£ ņåŹļÅäļĪ£ ņä▒ņןĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳Ļ▓ī ņČ®ļČäĒĢ£ ņ╣╝ļĪ£ļ”¼ņÖĆ ņśüņ¢æļČäņØä Ļ│ĄĻĖēĒĢ┤ņĢ╝ ĒĢśļŖöļŹ░, ņĀüņĀłĒĢ£ ņśüņ¢æĻ┤Ćļ”¼ļŖö ņĀĢņāüņĀüņØĖ ņä▒ņןļ░£ļŗ¼, Ļ░ÉņŚ╝ņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ņĀĆĒĢŁļĀź, ņĀüņĀłĒĢ£ ņŗĀĻ▓Į ņä▒ņłÖĻ│╝ ļ░£ļŗ¼ņØä ņ£äĒĢ┤ ļ¦żņÜ░ ņżæņÜöĒĢśļŗż(Hay, 2013; Lapillonne & Griffin, 2013; Seo, Kim, & Kim, 2016). ļö░ļØ╝ņä£ ņØśĒĢÖņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņĢłņĀĢņĀüņØĖ ĒĢ£ ļ¬©ļōĀ ļ»ĖņłÖņĢäļŖö ņ×¼Ēā£ĻĖ░Ļ░äņØ┤ļéś ņČ£ņāØ ņ▓┤ņżæĻ│╝ ņāüĻ┤ĆņŚåņØ┤ ņĀĢļ¦źņśüņ¢æĻ│╝ ņןĻ┤Ćņśüņ¢æņØä ļ│æĒ¢ēĒĢśļ®┤ņä£ ĒĢäņÜöĒĢ£ ņ╣╝ļĪ£ļ”¼ļź╝ ņČ®ļŗ╣ĒĢśĻ▓ī ļÉśļ®░(Gokmen et al., 2012), 34ņŻ╝ ļ»Ėļ¦īņØś ļ»ĖņłÖņĢäļŖö ļ╣©ļĀżļŖö ļģĖļĀźņŚÉ ĒĢ£Ļ│äĻ░Ć ņ׳ņ£╝ļ»ĆļĪ£ ņä▒ņłÖĒĢśĻĖ░Ļ╣īņ¦ĆļŖö ņ×ģņØ┤ļéś ņĮöļź╝ ĒåĄĒĢ┤ ņ£äĻ┤ĆņØä ļäŻņ¢┤ ņśüņ¢æņØä Ļ│ĄĻĖēĒĢśĻ▓ī ļÉ£ļŗż(Pi, 2008). ļ»ĖņłÖņĢäņŚÉĻ▓ī ņ׳ņ¢┤ ņśüņ¢æņØś ļ¬®ņĀüņØĆ ļČäļ¦ī Ēøä ņ▓½ ļ¬ć ņŻ╝ ļé┤ ņĀĢļ¦źņśüņ¢æņŚåņØ┤ ņןĻ┤Ćņśüņ¢æņ£╝ļĪ£ļ¦ī ĒĢäņÜöĒĢ£ ĻČīņן ņśüņ¢æļ¤ēņØä Ļ│ĄĻĖēĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ļŖö ņÖäņĀäņןĻ┤Ćņśüņ¢æņŚÉ ļÅäļŗ¼ĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓āņØ┤ļŗż(Hans, Pylipow, Long, Thureen, & Georgieff, 2009).
ĻĘĖļ¤¼ļéś ļ»ĖņłÖņĢäņŚÉĻ▓ī ņĀüņĀłĒĢ£ ņśüņ¢æņØä Ļ│ĄĻĖēĒĢśļŖö ļŹ░ļŖö ļ¦ÄņØĆ ļé£Ļ┤ĆņØ┤ ņ׳ļŗż. ņ×¼Ēā£ĻĖ░Ļ░äņØ┤ ņ¦¦Ļ│Ā ņČ£ņāØ ņ▓┤ņżæņØ┤ ņ×æņØäņłśļĪØ ņ£äņןĻ┤Ć ĻĖ░ļŖźņØ┤ ļ»ĖņłÖĒĢśĻ│Ā ņן ņÜ┤ļÅÖņØ┤ ņĀĆĒĢśļÉśņ¢┤ ņłśņ£Ā Ēøä ņ£ä ņĀĆļźśĻ░Ć ļ¦ÄņĢäņ¦ĆļŖö ņłśņ£ĀļČłļé┤ņä▒(feeding intolerance)ņØä ņ┤łļלĒĢ£ļŗż(Jang, 2011). ļ»ĖņłÖņĢäņØś ņןĻ┤Ćņśüņ¢æņŚÉ ļ░®ĒĢ┤Ļ░Ć ļÉśļŖö ļīĆĒæ£ņĀüņØĖ ņåīĒÖöĻĖ░ņןņĢĀļŖö ņłśņ£ĀļČłļé┤ņä▒Ļ│╝ Ļ┤┤ņé¼ņä▒ ņןņŚ╝(necrotizing enterocolitis)ņØ┤ļŗż(Shin, 2009). ņłśņ£ĀļČłļé┤ņä▒ņØĆ ņןĻ┤Ćņśüņ¢æņØä ņØ╝ņŗ£ņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņżæņ¦ĆĒĢśļ®┤ ļīĆļČĆļČä ĒśĖņĀäļÉśņ¦Ćļ¦ī ĻĘĖļ¦īĒü╝ ņłśņ£Āņ¦äĒ¢ēņØ┤ ļŖÉļĀżņĀĖ ņןĻ┤Ćņśüņ¢æņØ┤ ņ¦ĆņŚ░ļÉ£ļŗż(Moody, Schanler, Lau, & Shulman, 2000). ņןĻ┤Ćņśüņ¢æ ņ¦ĆņŚ░ņØĆ ņĀĢļ¦źņśüņ¢æ ĻĖ░Ļ░äņØä ļŖśļĀż ņĀĢļ¦źņśüņ¢æĻ┤ĆļĀ©Ļ░äņ¦łĒÖśņØś ņ£äĒŚśņØä ņ”ØĻ░Ćņŗ£ĒéżĻ│Ā, ņżæņŗ¼ņĀĢļ¦źĻ┤ĆņØä ĒĢäņÜöļĪ£ ĒĢśĻ▓ī ļÉśļ®░ ņØ┤ļĪ£ ņØĖĒĢ£ Ļ░ÉņŚ╝ ļō▒ ĒĢ®ļ│æņ”Ø ļ░£ņāØņØä ņ”ØĻ░Ćņŗ£Ēé©ļŗż(Ben, 2008). ļśÉ Ļ┤┤ņé¼ņä▒ ņןņŚ╝ņØĆ ņןņØś ņĀÉļ¦ē Ēś╣ņØĆ ņĀä ņĖĄņØś Ļ┤┤ņé¼ļĪ£ ņØĖĒĢśņŚ¼ ņāØĻĖ░ļŖö ņØæĻĖē ņåīĒÖöĻĖ░ ņ¦łĒÖśņ£╝ļĪ£ 90%Ļ░Ć ļ»ĖņłÖņĢäņŚÉņä£ ļ░£ņāØĒĢśļ®░ ņé¼ļ¦ØļźĀņØĆ 5-30%ņŚÉ ļŗ¼ĒĢśļŖö ņŗ¼Ļ░üĒĢ£ ņ¦łļ│æņØ┤ļŗż(Pi, 2008; Wu, Caplan, & Lin, 2012). ļö░ļØ╝ņä£ ļ»ĖņłÖņĢäņØś ņä▒ņן ļ░Å ļ░£ļŗ¼ņØä ņ£äĒĢ┤ ņØ┤ņÖĆ Ļ░ÖņØĆ ņåīĒÖöĻĖ░ņןņĢĀ ļ░Å ĒĢ®ļ│æņ”ØņØä ņĄ£ņåīĒÖöĒĢśļ®┤ņä£ ņןĻ┤Ćņśüņ¢æņØä ĒåĄĒĢ┤ ņČ®ļČäĒĢ£ ņ╣╝ļĪ£ļ”¼ļź╝ ņĀ£Ļ│ĄĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ļŖö ļ░®Ē¢źņ£╝ļĪ£ ņØ┤ļŻ©ņ¢┤ņĀĖņĢ╝ ĒĢ£ļŗż.
ņ£äĻ┤Ćņśüņ¢æņØä ĒĢśļŖö ĒÖśņ×ÉņŚÉĻ▓ī ņ׳ņ¢┤ņä£ Ļ░äĒśĖņé¼ļŖö ņĀüņĀĢļ¤ēņØś ņśüņ¢æņØä Ļ│ĄĻĖēĒĢśĻ│Ā ņåīĒÖöĻĖ░ņןņĢĀļź╝ ņĪ░ĻĖ░ņŚÉ ļ░£Ļ▓¼ĒĢśļŖö ļō▒ņØś ĒĢĄņŗ¼ņĀüņØĖ ņŚŁĒĢĀņØä ĒĢ£ļŗż(Bollineni & Minocha, 2011). ņåīĒÖöĻĖ░ņןņĢĀļź╝ ņĪ░ĻĖ░ļ░£Ļ▓¼ĒĢśĻĖ░ ņ£äĒĢ┤ ņØ╝ļ░śņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņŗĀņāØņĢäņżæĒÖśņ×Éņŗż Ļ░äĒśĖņé¼ļōżņØĆ ņ£äĻ┤Ćņśüņ¢æņØä ĒĢśļŖö ļ»ĖņłÖņĢäņŚÉĻ▓ī ļ¦ż ņłśņ£Ā ņ¦üņĀä ņ£ä ņ×öļźśņØś ņ¢æĻ│╝ ņ¢æņāüņØä ĒÖĢņØĖĒĢśņŚ¼ ņ£ä ļ░░ņČ£ņØś ņ¦ĆņŚ░ ņŚ¼ļČĆļź╝ ĒÖĢņØĖĒĢśĻ│Ā ņ׳ļŗż(Gregory & Connolly, 2012). ĻĘĖļ¤¼ļéś ņ£ä ņ×öļźśļ¤ēņØĆ ĒÖśņ×ÉņØś ņ▓┤ņ£äļéś ņłśņ£Ā ņóģļźś ļ░Å ņ£äĻ┤ĆņØś Ēü¼ĻĖ░, ņ£äņ╣śņŚÉ ļö░ļØ╝ ļŗ¼ļØ╝ņ¦ł ņłś ņ׳ņ£╝ļ®░(Li et al., 2014), Ļ┤┤ņé¼ņä▒ ņןņŚ╝ņØä ņŗ£ņé¼ĒĢśļŖö ņ£ä ņ×öļźśļ¤ēņØ┤ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ļ¦łļŗż ļŗżļź┤Ļ▓ī ļ│┤Ļ│ĀļÉśĻ│Ā ņ׳ņ¢┤ ĻĘĖ ĻĖ░ņżĆļÅä ļ¬ģĒÖĢĒĢśņ¦Ć ņĢŖļŗż(Bertino et al., 2009; Cobb, Carlo, & Ambalavanan, 2004;Mihatsch et al., 2002). ņØ┤ņ▓śļ¤╝ ņ£ä ņ×öļźśņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ĒĢ®ņØśļÉśņ¦Ć ņĢŖņØĆ ĻĖ░ņżĆņØ┤ļéś ĒŖ╣ņä▒ņ£╝ļĪ£ ņןĻ┤Ćņśüņ¢æņØ┤ ļČĆņĀüņĀłĒĢśĻ▓ī ņżæļŗ©ļÉśĻ▒░ļéś ņ¦ĆņŚ░ļÉśļ®┤ ņÖäņĀäņןĻ┤Ćņśüņ¢æņŚÉ ļÅäļŗ¼ĒĢśļŖö ņŗ£Ļ░äņØä ņ¦ĆņŚ░ņŗ£ĒéżļŖö Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ļź╝ Ļ░ĆņĀĖņś¼ ņłś ņ׳ļŗż(Li et al., 2014). ļśÉĒĢ£ ņ£ä ņ×öļźśņŚÉļŖö ņ£äņé░Ļ│╝ ņןĻ┤ĆņÜ┤ļÅÖņØś ņä▒ņłÖ ļ░Å ņ┤ēņ¦äņØä ļÅĢļŖö ĒÜ©ņåīļź╝ ĒżĒĢ©ĒĢśĻ│Ā ņ׳ļŖöļŹ░(Williams & Leslie, 2010), ĒØĪņØĖļÉ£ ņ£ä ņ×öļźśĻ░Ć ĒÅÉĻĖ░ļÉ£ļŗżļ®┤ ļ»ĖņłÖņĢäņØś ņ£äņןĻ┤ĆĻ│ä ņä▒ņłÖņŚÉ ļČĆņĀĢņĀüņØĖ ņśüĒ¢źņØä ļ»Ėņ╣Ā ņłś ņ׳ļŗż(Li et al., 2014). ĒŖ╣Ē׳ ņłśņ£Ā ņŻ╝ĻĖ░Ļ░Ć ņ¦¦ņØĆ ļ»ĖņłÖņĢäņØś Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ ĒĢśļŻ©ņŚÉ 8~12ĒÜī ļ░śļ│ĄņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ Ē¢ēĒĢ┤ņ¦Ćļ»ĆļĪ£ ļŹöņÜ▒ ļ¼ĖņĀ£Ļ░Ć ļÉĀ ņłś ņ׳ļŗż. ļö░ļØ╝ņä£ ļ»ĖņłÖņĢäņŚÉņä£ ņłśņ£Ā ņ¦üņĀä ļ¦żļ▓ł ņ£ä ņ×öļźśļź╝ ĒÖĢņØĖĒĢśļŖö ņŻ╝ĻĖ░ņĀü ņ£ä ņ×öļźś ĒÖĢņØĖ ļ░®ļ▓ĢņØĆ ĻĘĖ ĻĘ╝Ļ▒░Ļ░Ć ļČĆņĪ▒ĒĢśĻ│Ā ĒĢ┤ļĪ£ņÜĖ ņłśļÅä ņ׳ļŗżļŖö ļ╣äĒīÉņØ┤ ņ¦ĆņåŹņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņĀ£ĻĖ░ļÉśņ¢┤ ņÖöļŗż(Li et al., 2014;Parker et al., 2015).
ņĄ£ĻĘ╝ ĻĄŁņÖĖ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ņŚÉņä£ ņŻ╝ĻĖ░ņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņ£ä ņ×öļźśļź╝ ĒÖĢņØĖĒĢ£ Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ļ│┤ļŗż ņåīĒÖöĻĖ░ņןņĢĀņØś ņ×äņāüņĀü ņ¦ĢĒøäĻ░Ć ņ׳ļŖö Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ņŚÉļ¦ī ņ£ä ņ×öļźśļź╝ ĒÖĢņØĖĒĢ£ Ļ▓ĮņÜ░Ļ░Ć Ļ┤┤ņé¼ņä▒ ņןņŚ╝ ņ£äĒŚśņä▒ņØś ņ”ØĻ░Ć ņŚåņØ┤ ņÖäņĀäņןĻ┤Ćņśüņ¢æ ļÅäļŗ¼ņŗ£Ļ░äņØ┤ ļŹö ļ╣ĀļźĖ Ļ▓āņ£╝ļĪ£ ļ│┤Ļ│ĀļÉśņŚłļŗż(Riskin et al., 2017).Li ļō▒(2014)ņØĆ ļ╣äņ╣©ņŖĄņĀüņØĖ ņ×äņāüņĀü ņ¦ĢĒøäļź╝ ņŻ╝ĻĖ░ņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ļ¬©ļŗłĒä░ļ¦üĒĢśĻ│Ā, ņØ┤ ņ¦ĢĒøäļź╝ ĒåĄĒĢ┤ ņ£ä ņ×öļźś ņĖĪņĀĢ ņŚ¼ļČĆļź╝ Ļ▓░ņĀĢĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓āņØ┤ ļ░öļ×īņ¦üĒĢśļŗżĻ│Ā ņĀ£ņĢłĒĢśņśĆļŗż. ĻĘĖļ¤¼ļéś ĻĄŁļé┤ņŚÉņä£ļŖö ņĢäņ¦üĻ╣īņ¦Ć ņ¦Ćņ╣©ņØ┤ ļ¦łļĀ©ļÉśņ¦Ć ņĢŖņĢä ļīĆļČĆļČäņØś ņŗĀņāØņĢäņżæĒÖśņ×ÉņŗżņŚÉņä£ļŖö ņŻ╝ĻĖ░ņĀü ņ£ä ņ×öļźś ĒÖĢņØĖņØä ĒåĄĒĢ┤ ņןĻ┤Ćņśüņ¢æ ņ¦ĆņåŹ ļ░Å ņłśņ£ĀļČłļé┤ņä▒ņØ┤ļéś Ļ┤┤ņé¼ņä▒ ņןņŚ╝ņØś ņ¦ĆĒæ£ļĪ£ ĒÖ£ņÜ®ĒĢśĻ│Ā ņ׳ļŗż(Seo et al., 2016).
ņØ┤ņŚÉ ļ░śĒĢ┤ ļ│Ė ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ļīĆņāüļ│æņøÉņØĆ ņäĀĒ¢ēņŚ░ĻĄ¼ļź╝ ļ░öĒāĢņ£╝ļĪ£ ņĀäļ¼ĖĻ░ĆņØś ĒĢ®ņØśļź╝ ĒåĄĒĢ┤ 2017ļģä 1ņøöļČĆĒä░ ņłśņ£Ā ņĀä ņŻ╝ĻĖ░ņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņ£ä ņ×öļźśļź╝ ĒÖĢņØĖĒĢśļŹś ĻĖ░ņĪ┤ ņŗżļ¼┤ņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ┤ ņłśņ£ĀļČłļé┤ņä▒ņØś ņ×äņāüņĀü ņ¦ĢĒøäĻ░Ć ņ׳ļŖö Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ņŚÉļ¦ī ĒĢäņÜöņŗ£ ņ£ä ņ×öļźśļź╝ ĒÖĢņØĖĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓āņ£╝ļĪ£ ņŗżļ¼┤ņ¦Ćņ╣©ņØä ļ│ĆĻ▓ĮĒĢśņŚ¼ ņŗ£Ē¢ēĒĢśĻ│Ā ņ׳ļŗż. ņØ┤ņŚÉ ņŗżļ¼┤ ļ│ĆĻ▓Į ņĀä ņŻ╝ĻĖ░ņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņ£ä ņ×öļźśļź╝ ĒÖĢņØĖĒĢ£ ļ»ĖņłÖņĢäņÖĆ ņŗżļ¼┤ ļ│ĆĻ▓Į Ēøä ņ×äņāüņĀü ņ¦ĢĒøäĻ░Ć ņ׳ņØä Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ ĒĢäņÜöņŗ£ ņ£ä ņ×öļźśļź╝ ĒÖĢņØĖĒĢ£ ļ»ĖņłÖņĢäņØś ņÖäņĀäņןĻ┤Ćņśüņ¢æ ļÅäļŗ¼ņŗ£Ļ░ä, ņłśņ£ĀļČłļé┤ņä▒, Ļ┤┤ņé¼ņä▒ ņןņŚ╝ ļō▒Ļ│╝ Ļ░ÖņØĆ ņ×äņāüĻ▓░Ļ│╝ļź╝ ļ╣äĻĄÉĒĢśņŚ¼ ĻĘĖ ņ£ĀņÜ®ņä▒ņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ļ╣äĒīÉņĀü ĻĘ╝Ļ▒░ļź╝ ļ¦łļĀ©ĒĢśĻ│Āņ×É ĒĢ£ļŗż.
ļ│Ė ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ļŖö ņ£äĻ┤Ćņśüņ¢æņØä ĒĢśļŖö ļ»ĖņłÖņĢäņØś ņ£ä ņ×öļźś ĒÖĢņØĖņØś ņ£ĀņÜ®ņä▒ņØä ĒÅēĻ░ĆĒĢśĻĖ░ ņ£äĒĢśņŚ¼ ņŻ╝ĻĖ░ņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņ£ä ņ×öļźśļź╝ ĒÖĢņØĖĒĢ£ ļ»ĖņłÖņĢäņÖĆ ĒĢäņÜöņŗ£ ņ£ä ņ×öļźśļź╝ ĒÖĢņØĖĒĢ£ ļ»ĖņłÖņĢäņØś ņ×äņāüĻ▓░Ļ│╝ļź╝ ļ╣äĻĄÉĒĢ£ ĒøäĒ¢źņĀü ņĮöĒśĖĒŖĖ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ņØ┤ļŗż.
ļ»ĖņłÖņĢäņŚÉņä£ ņ£äĻ┤Ćņśüņ¢æ(gavage feeding) ņĀüņØæņ”ØņØĆ ņ×¼Ēā£ĻĖ░Ļ░ä 34ņŻ╝ ļ»Ėļ¦īņØś ļ»ĖņłÖņĢä, ļ╣ĀļŖöļŹ░ ļ¦ÄņØĆ ņŚÉļäłņ¦Ćļź╝ ņåīļ╣äĒĢśņŚ¼ ņל ņ×ÉļØ╝ņ¦Ć ļ¬╗ĒĢśļŖö ļ»ĖņłÖņĢä, ļ╣©ĻĖ░(sucking)ņÖĆ ņŚ░ĒĢś(swallowing)Ļ░Ć ņל ļÉśņ¦Ć ļ¬╗ĒĢśļŖö ņŗĀņāØņĢä(ņśł, ĻĘ╝ļ¼┤ļĀźņ”Ø, ņĀĆņé░ņåīņä▒ļćīļ│æņ”Ø), ĒśĖĒØĪņłśĻ░Ć 60~80ĒÜī/ļČä ņØ┤ņāüņØĖ Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ņØ┤ļŗż(Pi, 2008). ņØ┤ņŚÉ ļ│Ė ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ļŖö 2015ļģä 12ņøöļČĆĒä░ 2017ļģä 10ņøöĻ╣īņ¦Ć ņä£ņÜĖ ņåīņ×¼ ņØ╝Ļ░£ ņāüĻĖēņóģĒĢ®ļ│æņøÉ ņŗĀņāØņĢäņżæĒÖśņ×ÉņŗżņŚÉ ņ×ģņøÉĒĢ£ ļ»ĖņłÖņĢäļōż ņżæ ņČ£ņāØņ▓┤ņżæĻ│╝ ņāüĻ┤ĆņŚåņØ┤ ņ×¼Ēā£ĻĖ░Ļ░ä 34ņŻ╝ ļ»Ėļ¦īņ£╝ļĪ£ ņČ£ņāØĒĢśņŚ¼ ņ£äĻ┤Ćņśüņ¢æņØä ņŗ£Ē¢ēĒĢ£ ļ»ĖņłÖņĢäļź╝ ļīĆņāüņ£╝ļĪ£ ĒĢśņśĆļŗż. ņŻ╝ĻĖ░ņĀü ņ£ä ņ×öļźś ĒÖĢņØĖĻĄ░(routine evaluation of gastric residuals; RGRĻĄ░)ņØĆ 2015ļģä 12ņøöļČĆĒä░ 2016ļģä 10ņøöĻ╣īņ¦Ć ņ×ģņøÉĒĢ£ ļīĆņāüņ×ÉļĪ£ ĒĢśņśĆĻ│Ā, ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ļīĆņāüļ│æņøÉņØś ļ»ĖņłÖņĢä ņ£äĻ┤Ćņśüņ¢æ ņŗżļ¼┤Ļ░Ć ĒĢäņÜöņŗ£ ņ£ä ņ×öļźś ĒÖĢņØĖņ£╝ļĪ£ ļ│ĆĻ▓ĮļÉ£ 2017ļģä 1ņøöļČĆĒä░ 10ņøöĻ╣īņ¦Ć ņ×ģņøÉĒĢ£ ļīĆņāüņ×Éļź╝ ĒĢäņÜöņŗ£ ņ£ä ņ×öļźś ĒÖĢņØĖĻĄ░(no-RGRĻĄ░)ņ£╝ļĪ£ ņäĀņĀĢĒĢśņśĆļŗż. ļīĆņāüņ×É ņĀ£ņÖĖĻĖ░ņżĆņØĆ ĻĖ░ņĀĆņ¦łĒÖśņ£╝ļĪ£ ņé¼ļ¦ØĒĢ£ ļ»ĖņłÖņĢä ļ░Å ņןĻ┤Ćņśüņ¢æņØś ņ¦ĆņŚ░Ļ│╝ ņŚ░Ļ┤ĆļÉ£ ņäĀņ▓£ņä▒ ņ¦łĒÖś(ņäĀņ▓£ņä▒ ĻĖ░Ļ┤ĆņŗØļÅäļłäĻ┤Ć, ņäĀņ▓£ņä▒ ĒÜĪĻ▓®ļ¦ēĒāłņן, ņäĀņ▓£ņä▒ ļ¦źņ╝łĻ▓īņŗż, ņäĀņ▓£ņä▒ Ēā£ļ│Ć ļ¦łĻ░£ ņ”ØĒøäĻĄ░ ļō▒)ņØä Ļ░Ćņ¦ä ļ»ĖņłÖņĢäņØ┤ļŗż. ņØ┤ ĒÖśņ×ÉļōżņØś Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ņŚÉļŖö ĻĖ░ņĀĆņ¦łĒÖśņ£╝ļĪ£ ņØĖĒĢ┤ ņ£ä ņ×öļźśņØś ļ│ĆĒÖöĻ░Ć ņ╗ż ņ£ä ņ×öļźś ĒÖĢņØĖ ļ░®ļ▓ĢņŚÉ ļö░ļźĖ ņ×äņāüņĀü ņ░©ņØ┤ļź╝ ļ╣äĻĄÉĒĢĀ ņłś ņŚåņ¢┤ņä£ ļīĆņāüņŚÉņä£ ņĀ£ņÖĖĒĢśņśĆļŗż.
ļīĆņāüņ×É ņłśļŖö G-power 3.1ņØä ņØ┤ņÜ®ĒĢśņŚ¼ ņ£ĀņØśņłśņżĆ(╬▒) .05, Ļ▓ĆņĀĢļĀź(1-╬▓) .80, ņäĀĒ¢ēņŚ░ĻĄ¼(Riskin et al., 2017)ņØś Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ļź╝ ņ░ĖņĪ░ĒĢśņŚ¼ Ļ│äņé░ĒĢ£ ĒÜ©Ļ│╝Ēü¼ĻĖ░(d).42ļĪ£ ĒĢśņśĆņØä ļĢī Ļ░ü ĻĄ░ļŗ╣ 93ļ¬ģņØ┤ ņé░ņČ£ļÉśņŚłņ£╝ļéś, ĒāłļØĮļźĀ 10%ļź╝ Ļ│ĀļĀżĒĢśņŚ¼ ņŻ╝ĻĖ░ņĀü ņ£ä ņ×öļźś ĒÖĢņØĖĒĢ£ ļīĆņāüņ×É 104ļ¬ģ, ĒĢäņÜöņŗ£ ņ£ä ņ×öļźśļź╝ ĒÖĢņØĖĒĢ£ ļīĆņāüņ×É 104ļ¬ģņØä ĒżĒĢ© ņ┤Ø 208ļ¬ģņØś ņ×ÉļŻīļź╝ ņĪ░ņé¼ĒĢśņśĆļŗż. Ļ░ü ĻĄ░ņØś ļīĆņāüņ×É ņłśņ¦æļ░®ļ▓ĢņØĆ RGRĻĄ░ņŚÉņä£ļŖö 2016ļģä 10ņøöļČĆĒä░ ņäĀņĀĢĻĖ░ņżĆņŚÉ ļ¦×ļŖö ļīĆņāüņ×Éļź╝ ņŚŁļ░®Ē¢źņ£╝ļĪ£ ņłśņ¦æĒĢśņŚ¼ 104ļ¬ģņØ┤ ļÉĀ ļĢīĻ╣īņ¦Ć ļ¬©ņ¦æĒĢśņśĆĻ│Ā, no-RGRĻĄ░ņØś Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ņŚÉļŖö 2017ļģä 1ņøöļČĆĒä░ ņ░©ļĪĆļīĆļĪ£ 104ļ¬ģņØ┤ ļÉĀ ļĢīĻ╣īņ¦Ć ņ░©ļĪĆļīĆļĪ£ ņłśņ¦æĒĢśņśĆļŗż.
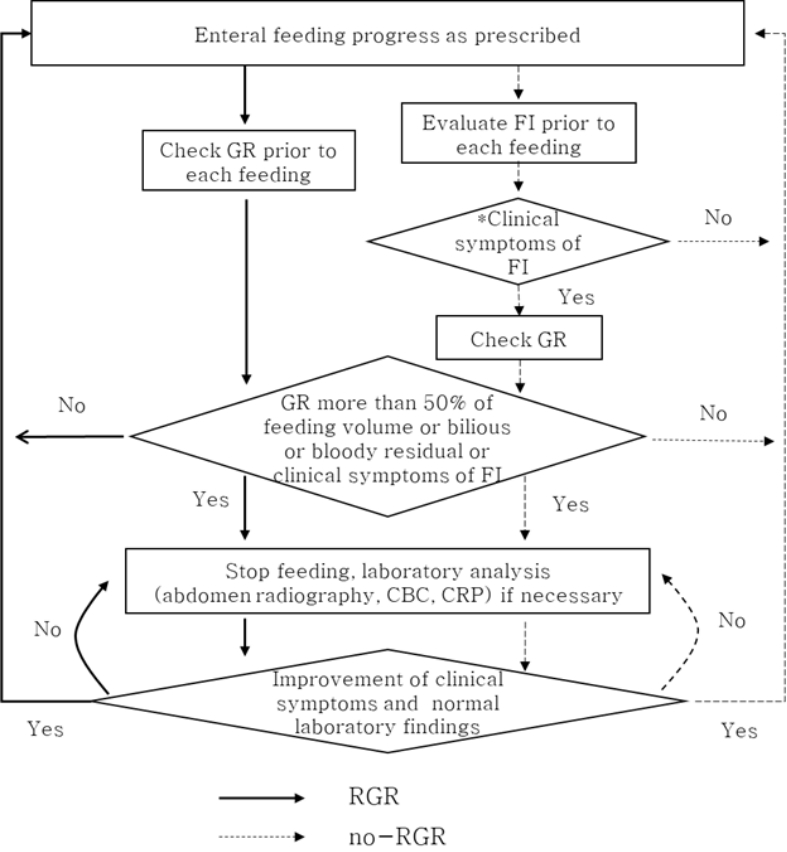
ņ£ä ņ×öļźś(gastric residual)ļ×Ć ņØ╝ņĀĢ ņŗ£Ļ░ä Ļ░äĻ▓® ĒøäņŚÉ ņ£äņןņŚÉ ļé©ņĢäņ׳ļŖö ņÜ░ņ£ĀņØś ņ¢æņØä ņĖĪņĀĢĒĢ£ Ļ▓āņ£╝ļĪ£(Abiramalatha, Thanigainathan, & Balakrishnan, 2019), ļ│Ė ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ņŚÉņä£ļŖö ļŗ┤ļŗ╣ Ļ░äĒśĖņé¼Ļ░Ć ņłśņ£Ā ņ¦üņĀä ņ£äĻ┤ĆņØä ĒåĄĒĢ┤ ņŻ╝ņé¼ĻĖ░ļĪ£ ĒØĪņØĖĒĢśņŚ¼ ļ░░ņČ£ļÉ£ ņ£ä ļé┤ņÜ®ļ¼╝ņØä ņØśļ»ĖĒĢ£ļŗż. Ļ░ü ĻĄ░ņØś ņ£ä ņ×öļźś ĒÖĢņØĖ ļ░®ļ▓ĢņØĆ Figure 1Ļ│╝ Ļ░Öļŗż. ņŻ╝ĻĖ░ņĀü ņ£ä ņ×öļźś ĒÖĢņØĖĻĄ░ņØĆ ņłśņ£Ā ņ¦üņĀä ļ¦żļ▓ł ņ£ä ņ×öļźśļź╝ ĒÖĢņØĖĒĢśņśĆĻ│Ā, ĒĢäņÜö ņŗ£ ņ£ä ņ×öļźś ĒÖĢņØĖĻĄ░ņØĆ ļ│ĄļČĆĒīĮļ¦īņØ┤ļéś ņןņØī ņĀĆĒĢś, ĻĄ¼ĒåĀ ļō▒ ņłśņ£ĀļČłļé┤ņä▒ņØś ņ×äņāü ņ¦ĢĒøäĻ░Ć ņ׳ļŖö Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ņŚÉļ¦ī ņ£ä ņ×öļźśļź╝ ĒÖĢņØĖĒĢśņśĆļŗż. ĒĢ┤ļŗ╣ļ│æņøÉņØś ļ│ĆĻ▓ĮļÉ£ ņ£ä ņ×öļźś ĒÖĢņØĖļ░®ļ▓ĢņØĆ Li ļō▒(2014)ņØś ŌĆ£Feeding algorithm for preterm infantsŌĆØ ļ░Å ņŗĀņāØņĢäņ¦äļŻīņ¦Ćņ╣© ņĀ£2ĒīÉ(Pi, 2008)ņØä ĒåĀļīĆļĪ£ ļ»ĖņłÖņĢä ņĀäļ¼ĖņØś 2ņØĖĻ│╝ ņŗĀņāØņĢäņżæĒÖśņ×Éņŗż ņĀäļ¼ĖĻ░äĒśĖņé¼ 1ņØĖņØ┤ ĒĢ┤ļŗ╣ ņŗĀņāØņĢäņżæĒÖśņ×ÉņŗżņØś ņāüĒÖ®ņŚÉ ļ¦×Ļ▓ī ņłśņĀĢ ļ░Å Ļ▓ĆĒåĀļź╝ Ļ▒░ņ│É ļ│ĆĻ▓ĮĒĢ£ Ēøä 2017ļģä 1ņøöļČĆĒä░ ņŗ£Ē¢ēĒĢśĻ│Ā ņ׳ņ£╝ļ®░, Ļ░ü ĻĄ░ņØś ņןĻ┤Ćņśüņ¢æ ņ¦Ćņ╣©ņØĆ ņ£ä ņ×öļźś ĒÖĢņØĖ ļ░®ļ▓ĢņŚÉ Ļ┤ĆĻ│äņŚåņØ┤ ļÅÖņØ╝ĒĢśļŗż.
ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ ļīĆņāüņ×ÉņØś ņØ╝ļ░śņĀü ĒŖ╣ņä▒ņ£╝ļĪ£ ņä▒ļ│ä, ņ×¼Ēā£ĻĖ░Ļ░ä, ņĢäĒöäĻ░Ć ņĀÉņłś, ņČ£ņāØ ņŗ£ ņ▓┤ņżæ, ĒśĖĒØĪĻ│żļ×Ćņ”ØĒøäĻĄ░, ĻĖ░Ļ┤Ćņ¦ĆĒÅÉņØ┤ĒśĢņä▒ņ”Ø, ļÅÖļ¦źĻ┤ĆĻ░£ņĪ┤ņ”Ø, 2ļŗ©Ļ│ä ņØ┤ņāüņØś ļćīņŗżļé┤ņČ£Ēśł ļśÉļŖö ļćīņŗż ļé┤ ļ░▒ņ¦łņŚ░ĒÖöņ”Ø, ņłśņ£Ā ņóģļźś(ļ¬©ņ£Ā/ļČäņ£Ā/Ēś╝ĒĢ®), ņÖäņĀäņןĻ┤Ćņśüņ¢æņØ╝ņŚÉ ļÅäļŗ¼ĒĢĀ ļĢīĻ╣īņ¦Ć ņ£ä ņ×öļźś ĒÖĢņØĖ ņØ╝ņłś(8ĒÜīļź╝ 1ņØ╝ļĪ£ Ļ│äņé░)ļź╝ ņĪ░ņé¼ĒĢśņśĆļŗż.
ļ│Ė ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ņŚÉņä£ ņ£ä ņ×öļźś ĒÖĢņØĖņØś ņ£ĀņÜ®ņä▒ņØä ĒÅēĻ░ĆĒĢśĻĖ░ ņ£äĒĢ┤ ņäĀĒ¢ēņŚ░ĻĄ¼ņŚÉņä£ ņé¼ņÜ®ĒĢ£ ņ¦ĆĒæ£ņŚÉ ĻĘ╝Ļ▒░ĒĢśņŚ¼ ņןĻ┤Ćņśüņ¢æĻ│╝ Ļ┤ĆļĀ©ļÉ£ ņ×äņāüĻ▓░Ļ│╝ļź╝ ņĪ░ņé¼ĒĢśņśĆļŗż(Riskin et al., 2017;Torrazza et al., 2015). ĒĢ┤ļŗ╣ ņ×äņāüĻ▓░Ļ│╝ļĪ£ļŖö ņÖäņĀäņןĻ┤Ćņśüņ¢æ ļÅäļŗ¼ņŗ£Ļ░ä, ļÅäļŗ¼ ņŗ£ ņ▓┤ņżæ, ņłśņ£ĀļČłļé┤ņä▒ ļ░£ņāØ ļ╣łļÅä, ņČ£ņāØ Ēøä ņ▓┤ņżæņØ┤ ņżäņ¢┤ļōżļŗżĻ░Ć ļŗżņŗ£ ĒÜīļ│ĄļÉśļ®┤ņä£ ņČ£ņāØ ļŗ╣ņŗ£ņØś ņ▓┤ņżæņŚÉ ņØ┤ļź┤ļŖöļŹ░ ņåīņÜöļÉśļŖö ņŗ£Ļ░äņØĖ ņ▓┤ņżæĒÜīļ│Ąņŗ£ĻĖ░, ņ×ģņøÉ ņżæ ņןĻ┤Ćņśüņ¢æ ņŗ£Ē¢ēĻĖ░Ļ░ä ļÅÖņĢł ņĀĢļ¦źņśüņ¢æņØä ĒĢ©Ļ╗ś Ē¢łļŹś ĻĖ░Ļ░ä(ņĀĢļ¦źņśüņ¢æĻĖ░Ļ░ä), ņĀĢļ¦źņśüņ¢æĻ┤ĆļĀ©Ļ░äņ¦łĒÖśĻ│╝ Ļ┤┤ņé¼ņä▒ ņןņŚ╝ ļ░£ņāØļ╣łļÅäļź╝ ņĪ░ņé¼ĒĢśņśĆļŗż. ņÖäņĀäņןĻ┤Ćņśüņ¢æ(full enteral feeding)ņØ┤ļ×Ć ņłśņĢĪļ│┤ņĪ░ņÜöļ▓Ģ ņŚåņØ┤ ņןĻ┤Ćņśüņ¢æļ¦īņ£╝ļĪ£ ĒĢäņÜöĒĢ£ ņłśļČä ļ░Å ņŚ┤ļ¤ēņØä Ļ│ĄĻĖēļ░øļŖö Ļ▓āņ£╝ļĪ£ ĒĢśļŻ© ņłśņ£Āļ¤ēņØ┤ 100 -150 mL/kgņŚÉ ļÅäļŗ¼ĒĢĀ ļĢīļź╝ ļ¦ÉĒĢ£ļŗż(Sisk, Lovelady, Gruber, Dillard, & OŌĆÖShea, 2008). ļ│Ė ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ņŚÉņä£ļŖö ĒĢśļŻ© ņłśņ£Āļ¤ēņØ┤ 120mL/kgņŚÉ ļÅäļŗ¼ĒĢĀ ļĢīļź╝ ņÖäņĀäņןĻ┤Ćņśüņ¢æņ£╝ļĪ£ ņĀĢņØśĒĢśņśĆļŗż. ņ▓┤ņżæņØĆ ļ│┤ņ£ĪĻĖ░ņŚÉ ņäżņ╣śļÉ£ ņ▓┤ņżæĻ│äļź╝ ņØ┤ņÜ®ĒĢśņŚ¼ ņĢ╝Ļ░äĻĘ╝ļ¼┤ņ×ÉĻ░Ć ņśżņĀäņŗ£Ļ░äņŚÉ ņĖĪņĀĢĒĢśņśĆļŗż. ņłśņ£ĀļČłļé┤ņä▒ņØĆ ļ¬ģĒÖĢĒ׳ ĒåĄņØ╝ļÉ£ ņĀĢņØśļź╝ ļé┤ļ”¼Ļ│Ā ņ׳ņ¦ĆļŖö ņĢŖņ£╝ļéś ļīĆĻ▓ī ļ░śļ│ĄņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ļ░£ņāØĒĢśļ®░, ļ│ĄļČĆĒīĮļ¦ī, ņ£ä ņ×öļźśņØś ņ”ØĻ░Ć, ļŗ┤ņ”ÖņØ┤ ņä×ņØĖ ņ£ä ņ×öļźś, ĻĄ¼ĒåĀ, Ēśłļ│Ć, ļ│ĄļČĆ X-ņäĀņāüņŚÉņä£ Ļ░ĆņŖżĒīĮļ¦ī ņåīĻ▓¼, ļ¼┤ĒśĖĒØĪ, ņä£ļ¦ź ļō▒ņØś ņ×äņāüņåīĻ▓¼ņØä ļéśĒāĆļé┤ļ®░(Moody et al., 2000), ĒĢ®ļ│æņ”Øņ£╝ļĪ£ ņłśņ£Āļź╝ ņĀĢņ¦ĆĒĢśĻ▒░ļéś ņłśņ£Āļ¤ēņØś Ļ░Éņåī ļśÉļŖö ņłśņ£Ā Ļ░äĻ▓®ņØ┤ ļŖśņ¢┤ļéśļŖö Ļ▓āņØä ņØśļ»ĖĒĢ£ļŗż(Amendolia, 2011). ļ│Ė ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ņŚÉņä£ļŖö ņÖäņĀäņןĻ┤Ćņśüņ¢æ ļÅäļŗ¼ņŗ£Ļ░äĻ╣īņ¦Ć ļ│ĄļČĆĒīĮļ¦ī, ĻĄ¼ĒåĀ, Ēśłļ│Ć, ļ¼┤ĒśĖĒØĪ, ņä£ļ¦ź ļō▒ņØś ņ×äņāüņåīĻ▓¼ņ£╝ļĪ£ ņØĖĒĢ┤ 12ņŗ£Ļ░ä ņØ┤ņāü ņłśņ£Āļź╝ ņĀĢņ¦ĆĒĢ£ Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ļĪ£ ĒĢśņśĆļŗż. ņĀĢļ¦źņśüņ¢æĻ┤ĆļĀ©Ļ░äņ¦łĒÖśņØĆ ņ¦ĆņåŹņĀüņØĖ ļ╣ä Ļ▓Įņןņśüņ¢æņØä ļ░øļŖö ĒÖśņ×ÉņŚÉņä£ ļŗżļźĖ Ļ░äņ¦łĒÖśņØ┤ ņŚåņØīņŚÉļÅä ļŗ┤ņ”Ö ļ░░ņäżņØś Ļ░Éņåī Ēś╣ņØĆ ĻĖ░Ļ│äņĀü ĒÅÉņćäņŚÉ ņØśĒĢ£ ņ¦łĒÖśņ£╝ļĪ£ ņØ╝ļ░śņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ļŗżļźĖ ņøÉņØĖ ņŚåņØ┤ ņ¦üņĀæ ļ╣īļ”¼ļŻ©ļ╣ł ņłśņ╣śĻ░Ć 2~3mg/dL ņØ┤ņāü ņ”ØĻ░ĆĒĢĀ Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ļĪ£ ņ¦äļŗ©ĒĢ£ļŗż(Duro et al., 2011). ļ│Ė ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ņŚÉņä£ļŖö 2ņŻ╝ ņØ┤ņāüņØś ņĀĢļ¦źņśüņ¢æņØä ļ░øņØĆ ļ»ĖņłÖņĢä ņżæ ļŗżļźĖ Ļ░ÉņŚ╝, ļśÉļŖö ņäĀņ▓£ņĀü ņøÉņØĖņ£╝ļĪ£ ņäżļ¬ģļÉśņ¦Ć ņĢŖļŖö Ēśłņżæ ņ¦üņĀæļ╣īļ”¼ļŻ©ļ╣ł 2mg/dL ņØ┤ņāüņ£╝ļĪ£ ĒĢśņśĆļŗż. Ļ┤┤ņé¼ņä▒ ņןņŚ╝ņØĆ ļŗ┤ļŗ╣ņØśĻ░Ć Modified BellŌĆÖs staging criteriaņŚÉ ļö░ļØ╝ stage 2 ņØ┤ņāüņ£╝ļĪ£ ĒīÉņĀĢĒĢ£ Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ļź╝ ņØśļ»ĖĒĢ£ļŗż.
ļ│Ė ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ņØś ņ£żļ”¼ņĀü Ļ│ĀļĀżļź╝ ņ£äĒĢ┤ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ļīĆņāüļ│æņøÉ ĻĖ░Ļ┤Ćņ£żļ”¼ņŗ¼ņØśņ£äņøÉĒÜīņØś ņŖ╣ņØĖ(ņŖ╣ņØĖļ▓łĒśĖ 2017-12-092)Ļ│╝ ļÅÖņØś ļ®┤ņĀ£ ņŖ╣ņØĖņØä ļ░øņØĆ Ēøä, ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ļīĆņāüļ│æņøÉņØś ņØśļ¼┤ĻĖ░ļĪØĒīĆņŚÉ ņØśļŻīņĀĢļ│┤ņ×ÉļŻī ņÜöņ▓Łņä£ ļ░Å Ļ░£ņØĖ ņĀĢļ│┤ ļ│┤ĒśĖ ņä£ņĢĮņä£ļź╝ ņ×æņä▒ĒĢśņŚ¼ ņĀ£Ļ│Ąļ░øņØĆ ņ×ÉļŻī ļé┤ņŚÉņä£ ņłśņ¦æĒĢśņśĆļŗż. ņØśļ¼┤ĻĖ░ļĪØņØĆ ņ×ģņøÉ ņŗ£ ļ│┤ĒśĖņ×ÉĻ░Ć ņØśļ¼┤ĻĖ░ļĪØ ņŚ┤ļ×īņØä ļÅÖņØśĒĢ£ ļ»ĖņłÖņĢäļĪ£ ņĀ£ĒĢ£ļÉśņ¢┤ ņ׳ņ¢┤ ņŚ┤ļ×īņØ┤ Ļ░ĆļŖźĒĢ£ ļīĆņāüņ×ÉņØś ņ×ÉļŻīļ¦ī ņłśņ¦æĒĢśņśĆļŗż. ņ×ÉļŻīņłśņ¦æņØĆ 2019ļģä 1ņøöļČĆĒä░ 4ņøöĻ╣īņ¦Ć ļ│Ė ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ņ×ÉĻ░Ć ņØśļ¼┤ĻĖ░ļĪØņØä Ļ▓ĆĒåĀĒĢśņŚ¼ ņ×ÉļŻīļź╝ ņłśņ¦æĒĢśņśĆĻ│Ā, ņłśņ¦æļÉ£ ņ×ÉļŻīļŖö ņĢöĒśĖ ņ▓śļ”¼ĒĢśņŚ¼ ņ×ĀĻĖł ņןņ╣śĻ░Ć ņ׳ļŖö Ļ││ņŚÉ ļ│┤Ļ┤ĆĒĢśĻ│Ā, ļČäņäØ ĒøäņŚÉļŖö Ļ┤ĆļĀ© ļ▓ĢĻĘ£ ļ░Å ĻĖ░Ļ┤Ć ĻĘ£ņĀĢņŚÉ ļö░ļØ╝ ņØ╝ņĀĢ ĻĖ░Ļ░ä ļ│┤Ļ┤Ć Ēøä ļČäņćä ĒÅÉĻĖ░ ņ▓śļ”¼ļÉĀ ņśłņĀĢņØ┤ļŗż.
ņłśņ¦æļÉ£ ņ×ÉļŻīļŖö SPSS win 21.0 ĒöäļĪ£ĻĘĖļשņØä ņØ┤ņÜ®ĒĢśņŚ¼ ņ£ĀņØśņłśņżĆ .05ņłśņżĆņŚÉņä£ ļČäņäØĒĢśņśĆļŗż. ļīĆņāüņ×ÉņØś ĒŖ╣ņä▒Ļ│╝ ņ£ĀņÜ®ņä▒ ĒÅēĻ░ĆņŚÉ ņé¼ņÜ®ļÉ£ ņ×äņāüĻ▓░Ļ│╝ņØś ņĀĢĻĘ£ņä▒ņØĆ Kolmogorov-SmirnovļĪ£ ĒÖĢņØĖĒĢśņśĆņ£╝ļ®░, ņĀĢĻĘ£ņä▒ņØä ļ¦īņĪ▒ĒĢśņ¦Ć ņĢŖņĢä ņżæņ£äņłśņÖĆ ņé¼ļČäņ£äņłś ļ▓öņ£ä, ļ╣łļÅäņÖĆ ļ░▒ļČäņ£©ļĪ£ ņĀ£ņŗ£ĒĢśņśĆļŗż. ļæÉ ĻĄ░ ļīĆņāüņ×ÉņØś ĒŖ╣ņä▒ņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ļÅÖņ¦łņä▒Ļ▓ĆņĀĢņØĆ Mann whitney U test, chi-squared test, ļśÉļŖö FisherŌĆÖs exact testļź╝ ņØ┤ņÜ®ĒĢśņŚ¼ ļČäņäØĒĢśņśĆļŗż. ņ£ä ņ×öļźś ĒÖĢņØĖņØś ņ£ĀņÜ®ņä▒ ĒÅēĻ░Ćļź╝ ņ£äĒĢ┤ ļæÉ ĻĄ░Ļ░ä ņ×äņāüĻ▓░Ļ│╝(ņÖäņĀäņןĻ┤Ćņśüņ¢æ ļÅäļŗ¼ņŗ£Ļ░ä, ņÖäņĀäņןĻ┤Ćņśüņ¢æ ļÅäļŗ¼ ņŗ£ ņ▓┤ņżæ, ņłśņ£ĀļČłļé┤ņä▒ ļ░£ņāØ ļ╣łļÅä, ņ▓┤ņżæĒÜīļ│Ąņŗ£ĻĖ░, ņĀĢļ¦źņśüņ¢æĻĖ░Ļ░ä, ņĀĢļ¦źņśüņ¢æĻ┤ĆļĀ©Ļ░äņ¦łĒÖśĻ│╝ Ļ┤┤ņé¼ņä▒ ņןņŚ╝ ļ░£ņāØ ļ╣łļÅä)ņØś ņ░©ņØ┤ļŖö Mann whitney U test, chisquared test, ļśÉļŖö FisherŌĆÖs exact testļĪ£ ļČäņäØĒĢśņśĆļŗż.
ļæÉ ĻĄ░ņØś ņä▒ļ│ä, ņ×¼Ēā£ĻĖ░Ļ░ä, ņĢäĒöäĻ░Ć ņĀÉņłś, ņČ£ņāØ ņŗ£ ņ▓┤ņżæņØĆ ĒåĄĻ│äņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņ£ĀņØśĒĢ£ ņ░©ņØ┤Ļ░Ć ņŚåņŚłļŗż. ļæÉ ĻĄ░ņØś ņ▓┤ņżæļ│ä ļ╣äņ£© ļśÉĒĢ£ ĒåĄĻ│äņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņ░©ņØ┤Ļ░Ć ņŚåņŚłļŗż. ĻĖ░ņĀĆļÅÖļ░śņ¦łĒÖśņ£╝ļĪ£ ĒśĖĒØĪĻ│żļ×Ćņ”ØĒøäĻĄ░, ĻĖ░Ļ┤Ćņ¦ĆĒÅÉņØ┤ĒśĢņä▒ņ”Ø, ļÅÖļ¦źĻ┤ĆĻ░£ņĪ┤ņżæ, ļćīņŗżļé┤ņČ£Ēśł ļśÉļŖö ļ░▒ņ¦ł ņŚ░ĒÖöņ”ØņØś ļ╣äņ£©ļÅä ĒåĄĻ│äņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņ£ĀņØśĒĢ£ ņ░©ņØ┤Ļ░Ć ņŚåņŚłļŗż.
ņłśņ£Ā ĒŖ╣ņä▒ņØä ņé┤ĒÄ┤ļ│┤ļ®┤ ņłśņ£Ā ņóģļźśļŖö ļæÉ ĻĄ░ ļ¬©ļæÉ Ēś╝ĒĢ®ņłśņ£Ā ļ╣łļÅäĻ░Ć Ļ░Ćņן ļåÆņĢśņ£╝ļ®░, ĒåĄĻ│äņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņ£ĀņØśĒĢ£ ņ░©ņØ┤Ļ░Ć ņŚåņŚłļŗż. ņÖäņĀäņןĻ┤Ćņśüņ¢æ ļÅäļŗ¼ņŗ£Ļ░äĻ╣īņ¦Ć ņ£ä ņ×öļźś ĒÖĢņØĖ ņØ╝ņłśļź╝ ļ╣äĻĄÉĒĢ£ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝, ņŻ╝ĻĖ░ņĀü ņ£ä ņ×öļźś ĒÖĢņØĖĻĄ░(RGRĻĄ░)ņØś ņ£ä ņ×öļźś ĒÖĢņØĖ ņØ╝ņłśļŖö 4.5ņØ╝, ĒĢäņÜöņŗ£ ņ£ä ņ×öļźś ĒÖĢņØĖĻĄ░(no-RGRĻĄ░)ņØś ņ£ä ņ×öļźś ĒÖĢņØĖ ņØ╝ņłśļŖö 0.3ņØ╝ļĪ£ ļæÉ ĻĄ░Ļ░ä ņ£ĀņØśĒĢ£ ņ░©ņØ┤ļź╝ ļ│┤ņśĆļŗż(p <.001)(Table 1).
ņ£ä ņ×öļźś ĒÖĢņØĖņØś ņ£ĀņÜ®ņä▒ ĒÅēĻ░Ćļź╝ ņ£äĒĢ£ ņ×äņāüĻ▓░Ļ│╝ ļ╣äĻĄÉ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ļŖö Table 2ņŚÉ ņĀ£ņŗ£ĒĢśņśĆļŗż. ņÖäņĀäņןĻ┤Ćņśüņ¢æ ļÅäļŗ¼ņŗ£Ļ░äņØĆ ļæÉ ĻĄ░Ļ░ä ĒåĄĻ│äņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņ£ĀņØśĒĢ£ ņ░©ņØ┤Ļ░Ć ņŚåņŚłļŗż. ļ»ĖņłÖņĢäļź╝ ņ▓┤ņżæļ│äļĪ£ ļéśļłĀņä£ ļ╣äĻĄÉĒĢ£ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ ņ┤łĻĘ╣ņåīņĀĆņ▓┤ņżæņČ£ņāØņĢäņŚÉņä£ RGRĻĄ░ņØś ņÖäņĀäņןĻ┤Ćņśüņ¢æ ļÅäļŗ¼ņŗ£Ļ░äņØĆ 32.5ņØ╝, no-RGRĻĄ░ņØĆ 21.0ņØ╝ļĪ£ ĒĢäņÜöņŗ£ ņ£ä ņ×öļźś ĒÖĢņØĖĻĄ░ņŚÉ ņÖäņĀäņןĻ┤Ćņśüņ¢æ ļÅäļŗ¼ņŗ£Ļ░äņØ┤ 11.5ņØ╝ ļŹö ņ¦¦ņĢśņ£╝ļéś ĒåĄĻ│äņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņ£ĀņØśĒĢ£ ņ░©ņØ┤ļŖö ņŚåņŚłļŗż. ņÖäņĀäņןĻ┤Ćņśüņ¢æ ļÅäļŗ¼ ņŗ£ ņ▓┤ņżæņØ┤ļéś ņ▓┤ņżæĒÜīļ│Ąņŗ£ĻĖ░, ņĀĢļ¦źņśüņ¢æĻĖ░Ļ░ä, ņĀĢļ¦źņśüņ¢æĻ┤ĆļĀ©Ļ░äņ¦łĒÖś ļ░£ņāØ ļ╣łļÅä ļśÉĒĢ£ ĒåĄĻ│äņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņ£ĀņØśĒĢ£ ņ░©ņØ┤Ļ░Ć ņŚåņŚłļŗż. ļæÉ ĻĄ░ņØś ņłśņ£ĀļČłļé┤ņä▒ ļ╣łļÅä ļśÉĒĢ£ ĒåĄĻ│äņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņ£ĀņØśĒĢ£ ņ░©ņØ┤Ļ░Ć ņŚåņŚłņ£╝ļ®░ ņ▓┤ņżæļ│ä ļ╣äņ£©ļÅä ĒåĄĻ│äņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņ£ĀņØśĒĢ£ ņ░©ņØ┤Ļ░Ć ņŚåņŚłļŗż. RGRĻĄ░ņŚÉņä£ Ļ┤┤ņé¼ņä▒ ņןņŚ╝ ļ░£ņāØĻ▒┤ņłśļŖö 5ļ¬ģņ£╝ļĪ£ ĻĘ╣ņåīņĀĆņ▓┤ņżæņČ£ņāØņĢäĻ░Ć 2ļ¬ģ, ņ┤łĻĘ╣ņåīņĀĆņ▓┤ņżæņČ£ņāØņĢäĻ░Ć 3ļ¬ģņØ┤ņŚłļŗż. No-RGRĻĄ░ņŚÉņä£ Ļ┤┤ņé¼ņä▒ ņןņŚ╝ ļ░£ņāØĻ▒┤ņłśļÅä 5ļ¬ģņ£╝ļĪ£ ļÅÖņØ╝ĒĢśņśĆĻ│Ā ĻĘ╣ņåīņĀĆņ▓┤ņżæņČ£ņāØņĢäĻ░Ć 1ļ¬ģ, ņ┤łĻĘ╣ņåīņĀĆņ▓┤ņżæņČ£ņāØņĢäĻ░Ć 4ļ¬ģņ£╝ļĪ£ ĒåĄĻ│äņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņ£ĀņØśĒĢ£ ņ░©ņØ┤ļŖö ņŚåņŚłļŗż.
ļ│Ė ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ļŖö ņ£äĻ┤Ćņśüņ¢æņØä ĒĢśļŖö ļ»ĖņłÖņĢäņŚÉņä£ ņŻ╝ĻĖ░ņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņ£ä ņ×öļźśļź╝ ĒÖĢņØĖĒĢ£ ĻĄ░Ļ│╝ ĒĢäņÜöņŗ£ ņ£ä ņ×öļźśļź╝ ĒÖĢņØĖĒĢ£ ĻĄ░ņØś ņ×äņāü Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ļź╝ ļ╣äĻĄÉĒĢśņŚ¼ ņ£ä ņ×öļźś ĒÖĢņØĖņØś ņ£ĀņÜ®ņä▒ņØä ĒÅēĻ░ĆĒĢśĻ│Āņ×É ņŗ£ļÅäļÉ£ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ļĪ£, ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ Ļ│Āņ░░Ļ│╝ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ņØś ņØśņØśļź╝ ļģ╝ņØśĒĢśĻ│Āņ×É ĒĢ£ļŗż.
ļ©╝ņĀĆ ļ│Ė ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ņŚÉņä£ ņÖäņĀäņןĻ┤Ćņśüņ¢æ ļÅäļŗ¼ņŗ£Ļ░äņØĆ ļæÉ ĻĄ░Ļ░ä ņ£ĀņØśĒĢ£ ņ░©ņØ┤Ļ░Ć ņŚåļŖö Ļ▓āņ£╝ļĪ£ ļéśĒāĆļé¼ļŗż. ĻĘĖļ¤¼ļéś ļ╣äļĪØ ĒåĄĻ│äņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņ£ĀņØśĒĢśņ¦ĆļŖö ņĢŖņĢśņ¦Ćļ¦ī ĻĘ╣ņåīņĀĆņ▓┤ņżæņČ£ņāØņĢä ļ░Å ņ┤łĻĘ╣ņåīņĀĆņ▓┤ņżæņČ£ņāØņĢäņØś ņÖäņĀäņןĻ┤Ćņśüņ¢æ ļÅäļŗ¼ņŗ£Ļ░äņØĆ no-RGRĻĄ░ņØ┤ RGRĻĄ░ļ│┤ļŗż Ļ░üĻ░ü 4.5ņØ╝Ļ│╝ 11.5ņØ╝ņØ┤ ļŹö ļŗ©ņČĢļÉ£ Ļ▓āņ£╝ļĪ£ ļéśĒāĆļéś, ņ×äņāüņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņØśļ»Ė ņ׳ļŖö Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ļØ╝ ņāØĻ░üļÉ£ļŗż. ļ│Ė ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ņŚÉņä£ņÖĆ Ļ░ÖņØ┤ ņČ£ņāØņ▓┤ņżæ 1,250ĻĘĖļש ņØ┤ĒĢś(ĒÅēĻĘĀ 924ĻĘĖļש)ņØś ĻĘ╣ņåīņĀĆņ▓┤ņżæņČ£ņāØņĢä ļ░Å ņ┤łĻĘ╣ņåīņĀĆņ▓┤ņżæņČ£ņāØņĢä 61ļ¬ģņØä ļīĆņāüņ£╝ļĪ£ RGRĻĄ░Ļ│╝ no-RGRĻĄ░ņ£╝ļĪ£ ļéśļłäņ¢┤ ļ╣äĻĄÉĒĢ£ Torrazza ļō▒(2015)ņØś ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ņŚÉņä£ļÅä ĒåĄĻ│äņĀü ņ░©ņØ┤ļŖö ņŚåņŚłņ¦Ćļ¦ī, no-RGRĻĄ░ņŚÉņä£ ņÖäņĀäņןĻ┤Ćņśüņ¢æ ļÅäļŗ¼ņŗ£Ļ░äņØ┤ 6ņØ╝ ļŹö ļ╣ĀļźĖ Ļ▓āņ£╝ļĪ£ ļéśĒāĆļé¼ļŗż. ļ░śļ®┤ ņ×¼Ēā£ĻĖ░Ļ░ä 34ņŻ╝ ņØ┤ĒĢśņØś ļ»ĖņłÖņĢä 472ļ¬ģņØä ļīĆņāüņ£╝ļĪ£ ĒĢ£ Riskin ļō▒(2017)ņØś ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ņŚÉņä£ļŖö ņÖäņĀäņןĻ┤Ćņśüņ¢æ ļÅäļŗ¼ņŗ£Ļ░äņØ┤ no-RGRĻĄ░ņØ┤ 8ņØ╝ļĪ£, RGRĻĄ░ņØś 9ņØ╝ļ│┤ļŗż ĒĢśļŻ© ļŹö ņ¦¦Ļ│Ā ĒåĄĻ│äņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņ£ĀņØśĒĢ£ Ļ▓āņ£╝ļĪ£ ļéśĒāĆļé¼ļŗż. ņÖäņĀäņןĻ┤Ćņśüņ¢æ ļÅäļŗ¼ ņ¦ĆņŚ░ņØĆ ļ»ĖņłÖņĢäņØś ņä▒ņן ļ░Å ņŗĀĻ▓ĮĻ│ä ļ░£ļŗ¼ņØä ļŹöļööĻ▓ī ĒĢĀ ļ┐É ņĢäļŗłļØ╝, ņĀĢļ¦źņśüņ¢æĻĖ░Ļ░äņØä ņŚ░ņןņŗ£ņ╝£ ņĀĢļ¦źņśüņ¢æĻ┤ĆļĀ©Ļ░äņ¦łĒÖś ļ░Å ņżæņŗ¼ņĀĢļ¦źĻ┤Ć ņéĮņ×ģņ£╝ļĪ£ ņØĖĒĢ£ Ļ░ÉņŚ╝, ņŗ¼ļ¦ēņé╝ņČ£, ĒśłņĀäņāēņĀäņØś ņ£äĒŚśņØä ņ”ØĻ░Ćņŗ£ĒéżļŖö ļō▒ ņŗ¼Ļ░üĒĢ£ ļČĆņ×æņÜ®ņØä ņ┤łļלĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ļŗż(Hermansen & Hermansen, 2005).Riskin ļō▒(2017)ņØĆ ņŻ╝ĻĖ░ņĀü ņ£ä ņ×öļźś ĒÖĢņØĖņØ┤ ņÖäņĀäņןĻ┤Ćņśüņ¢æ ļÅäļŗ¼ņØś ņ¦ĆņŚ░ļ┐É ņĢäļŗłļØ╝ ņ×ģņøÉĻĖ░Ļ░äļÅä ņŚ░ņןņŗ£ĒéżļŖö Ļ▓āņ£╝ļĪ£ ļ│┤Ļ│ĀĒĢ£ ļ░ö, ĒĢäņÜöņŗ£ņŚÉļ¦ī ņ£ä ņ×öļźśļź╝ ĒÖĢņØĖĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓āņØ┤ ņåīĒÖöĻĖ░Ļ│ä ļō▒ ļČĆņ×æņÜ®ņØä ļŹö ņ”ØĻ░Ćņŗ£Ēéżņ¦Ć ņĢŖļŖö ĒĢ£ ņĀüĻĘ╣ņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņ×äņāüņŚÉņä£ ņĀüņÜ®ĒĢĀ ĒĢäņÜöĻ░Ć ņ׳ņØä Ļ▓āņ£╝ļĪ£ ļ│┤ņØĖļŗż.
ņןĻ┤Ćņśüņ¢æ ņŗ£ ĒØöĒ׳ ļéśĒāĆļéĀ ņłś ņ׳ļŖö ņłśņ£ĀļČłļé┤ņä▒ ļ░£ņāØļ╣łļÅäļŖö ļæÉ ĻĄ░Ļ░ä ĒåĄĻ│äņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņ£ĀņØśĒĢ£ ņ░©ņØ┤ļź╝ ļ│┤ņØ┤ņ¦Ć ņĢŖņĢśļŗż. ņØ┤ļŖö ņŻ╝ĻĖ░ņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņ£ä ņ×öļźśļź╝ ĒÖĢņØĖĒĢśņ¦Ć ņĢŖņĢäļÅä ņ×äņāüņ¦ĢĒøäļź╝ ņל Ļ┤Ćņ░░ĒĢśļ®┤ ņłśņ£ĀļČłļé┤ņä▒ņØä ĒīÉļŗ©ĒĢśļŖö ļŹ░ ņ░©ņØ┤Ļ░Ć ņŚåņØīņØä ņØśļ»ĖĒĢ£ļŗż. ņ£ä ņ×öļźśļŖö ņ×öļźśļ¤ē ļ│┤ļŗżļŖö ĻĄ¼ĒåĀ, ņןņØīĻ░Éņåī, ļ│ĄļČĆĒīĮļ¦ī, ļ│ĄļČĆ ņāēņØś ļ│ĆĒÖö, ļ¼┤ĒśĖĒØĪ, ņä£ļ¦ź, ņ▓┤ņś©ņØś ļČłņĢłņĀĢĻ│╝ Ļ░ÖņØĆ ņ×äņāüņĀü ņ¦ĢĒøäĻ░Ć ļÅÖļ░śļÉśņŚłņØä ļĢī ņżæņÜöĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ļŗż(Lucchini, Bizzarri, Giampietro, & De Curtis, 2011). ņłśņ£Ā ņŻ╝ĻĖ░Ļ░Ć ņ¦¦ņØĆ ļ»ĖņłÖņĢäņŚÉĻ▓ī ņŻ╝ĻĖ░ņĀü ņ£ä ņ×öļźś ĒÖĢņØĖņØĆ ĒØĪņØĖņ£╝ļĪ£ ņØĖĒĢ£ ņĀÉļ¦ē ņåÉņāü Ļ░ĆļŖźņä▒ņØ┤ ņ׳Ļ│Ā(Torrazza et al., 2015), ĒØĪņØĖļÉ£ ņ£ä ņ×öļźśļź╝ ļŗżņŗ£ ņŻ╝ņ×ģĒĢśņ¦Ć ņĢŖĻ│Ā ļ▓äļ”┤ Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ ņ£ä ņ×öļźśņŚÉ ĒżĒĢ©ļÉ£ ņ£äņןĻ┤Ć ĒÜ©ņåī, ņ£ä ņä▒ņłÖņØä ņ┤ēņ¦äņŗ£ĒéżļŖö ĒśĖļź┤ļ¬¼ ļō▒ņØś ņåīņŗżļĪ£ ņØĖĒĢ┤ ļČĆņĀĢņĀüņØĖ ņśüĒ¢źņØä ņżä ņłś ņ׳ļŗż(Li et al., 2014).Kaur ļō▒(2015)ņØĆ ņłśņ£ĀļČłļé┤ņä▒ ĒÖĢņØĖ ļ░®ļ▓Ģņ£╝ļĪ£ ņŻ╝ĻĖ░ņĀü ņ£ä ņ×öļźś ĒÖĢņØĖļ│┤ļŗż ļ│ĄļČĆ ļæśļĀłļź╝ ņĖĪņĀĢĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓āņØ┤ Ļ┤┤ņé¼ņä▒ ņןņŚ╝ņØś ļ░£ņāØļźĀņØä ņ”ØĻ░Ćņŗ£Ēéżņ¦Ć ņĢŖņ£╝ļ®┤ņä£ ņÖäņĀäņןĻ┤Ćņśüņ¢æ ļÅäļŗ¼ņŗ£Ļ░äņØä ļŗ©ņČĢņŗ£ĒéżĻ│Ā ņłśņ£Ā ņżæ ļŗ©ņØ╝ņØä Ļ░Éņåīņŗ£ņ╝£ ļŹö ņ£ĀņÜ®ĒĢ£ ņ¦ĆĒæ£ļØ╝Ļ│Ā ĒĢśņśĆļŗż. ļö░ļØ╝ņä£ ļ╣äņ╣©ņŖĄņĀüņØĖ ņ×äņāü ņ¦ĢĒøäļź╝ ņŻ╝ĻĖ░ņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ļ¬©ļŗłĒä░ļ¦üĒĢśĻ│Ā, ņØ┤ ņ¦ĢĒøäļź╝ ĒåĄĒĢ┤ ņ£ä ņ×öļźś ņĖĪņĀĢ ņŚ¼ļČĆļź╝ Ļ▓░ņĀĢĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓āņØ┤ ļ░öļ×īņ¦üĒĢĀ Ļ▓āņ£╝ļĪ£ ņāØĻ░üļÉ£ļŗż.
ļæÉ ĻĄ░ņØś Ļ┤┤ņé¼ņä▒ ņןņŚ╝ ļ░£ņāØ ļ╣łļÅä ļśÉĒĢ£ ĒåĄĻ│äņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņ£ĀņØśĒĢ£ ņ░©ņØ┤Ļ░Ć ņŚåņŚłļŖöļŹ░, ņØ┤ļŖö ņäĀĒ¢ēņŚ░ĻĄ¼ļōż(Riskin et al., 2017;Torrazza et al., 2015)Ļ│╝ ņØ╝ņ╣śĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ņØ┤ļŗż. Ļ┤┤ņé¼ņä▒ ņןņŚ╝ņØĆ ļ»ĖņłÖņĢäņØś ņØæĻĖēņåīĒÖöĻĖ░ņ¦łĒÖśņ£╝ļĪ£ ņĪ░ĻĖ░ļ░£Ļ▓¼Ļ│╝ ņ╣śļŻīĻ░Ć ņżæņÜöĒĢśļ»ĆļĪ£(Pi, 2008), ļ¦ÄņØĆ ņŗĀņāØņĢäņżæĒÖśņ×ÉņŗżņŚÉņä£ ļ¦ż ņłśņ£Ā ņĀäņŚÉ ņ£ä ņ×öļźśļź╝ ĒÖĢņØĖĒĢśņŚ¼ ņ¢æĻ│╝ ņ¢æņāüņØä ĒåĀļīĆļĪ£ Ļ┤┤ņé¼ņä▒ ņןņŚ╝ņØä ņśłņĖĪĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ņØä Ļ▓āņØ┤ļØ╝ ņŚ¼Ļ▓©ņÖöļŗż(Parker et al., 2015). ĻĘĖļ¤¼ļéś Ļ┤┤ņé¼ņä▒ ņןņŚ╝ņØä ņŗ£ņé¼ĒĢśļŖö ņ£ä ņ×öļźśņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ĻĘ╝Ļ▒░Ļ░Ć ļČĆņĪ▒ĒĢśļŗż.Cobb ļō▒(2004)ņØĆ Ļ┤┤ņé¼ņä▒ ņןņŚ╝ņØ┤ ļ░£ņāØĒĢ£ ļ»ĖņłÖņĢäļŖö Ļ┤┤ņé¼ņä▒ ņןņŚ╝ņØä ņ¦äļŗ©ļ░øĻĖ░ 6ņØ╝ ņĀäņŚÉ ņ£ä ņ×öļźśļ¤ēņØ┤ ņ£ĀņØśĒĢśĻ▓ī ņ”ØĻ░ĆĒĢ£ļŗżĻ│Ā ĒĢśņśĆņ£╝ļéś,Bertino ļō▒(2009)ņØĆ Ļ┤┤ņé¼ņä▒ ņןņŚ╝ ņ¦äļŗ© 17ņØ╝ ņĀäņŚÉ ņ£ä ņ×öļźśļ¤ēņØ┤ ņ”ØĻ░ĆĒĢ£ļŗżĻ│Ā ĒĢśņśĆļŗż. ļśÉĒĢ£ ņ£ä ņ×öļźś ņāēņØ┤ ĒśłņĢĪņä▒ņØĖ Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ļŖö Ļ┤┤ņé¼ņä▒ ņןņŚ╝ņØś ņ¦ĆĒæ£Ļ░Ć ļÉĀ ņłś ņ׳ņ¦Ćļ¦ī(Bertino et al., 2009), ļŗ┤ņ”ÖņāēņØĖ Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ļŖö ļŗżļźĖ ņ×äņāü ņ¦ĢĒøäĻ░Ć ļÅÖļ░śļÉśņ¦Ć ņĢŖļŖöļŗżļ®┤ ņłśņ£ĀļČłļé┤ņä▒ņØ┤ļéś Ļ┤┤ņé¼ņä▒ ņןņŚ╝ņØś ņĪ░ĻĖ░ņ¦ĆĒæ£ļĪ£ļŖö ņŗĀļó░ĒĢśĻĖ░ ņ¢┤ļĀĄļŗżļŖö ļ│┤Ļ│ĀļÅä ņ׳ļŗż(Mihatsch et al., 2002). ņØ┤ņ▓śļ¤╝ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ļōżļ¦łļŗż Ļ┤┤ņé¼ņä▒ ņןņŚ╝ņØä ņŗ£ņé¼ĒĢśļŖö ņ£ä ņ×öļźśņØś ĒŖ╣ņä▒ņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ┤ ļŗżļź┤Ļ▓ī ņĀ£ņŗ£ĒĢśĻ│Ā ņ׳ņ¢┤ ĒĢ®ņØśļÉ£ ĻĘ╝Ļ▒░Ļ░Ć ņŚåļŖö ņŗżņĀĢņØ┤ļŗż. ļśÉ ņ£ä ņ×öļźśļ¤ēņØĆ ņĖĪņĀĢ ņŗ£ ļ»ĖņłÖņĢäņØś ņ▓┤ņ£ä, ņ£äĻ┤ĆņØś Ēü¼ĻĖ░, ņ£äņ╣ś, ĒØĪņØĖ ĻĖ░ņłĀ, ņłśņ£ĀņØś ņĀÉļÅäņŚÉ ļö░ļØ╝ ļŗ¼ļØ╝ņ¦ł ņłś ņ׳ņ¢┤ ņĀĢĒÖĢĒĢ£ ņĖĪņĀĢņØ┤ ņ¢┤ļĀżņøī Ļ┤┤ņé¼ņä▒ ņןņŚ╝ņØä ņśłņĖĪĒĢśļŖö ņ¦ĆĒæ£ļĪ£ņä£ ņŗĀļó░ņä▒ņØ┤ ļ¢©ņ¢┤ņ¦äļŗż(Li et al., 2014). ļö░ļØ╝ņä£ ņØ╝Ļ┤ĆļÉ£ ĒĢ®ņØśņĀÉņØ┤ ņŚåļŖö ņ£ä ņ×öļźś ĒŖ╣ņä▒ņØä ņÜ░ņäĀņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņ▓┤Ēü¼ĒĢśņŚ¼ ņłśņ£ĀļČłļé┤ņä▒Ļ│╝ Ļ┤┤ņé¼ņä▒ ņןņŚ╝ ņŚ¼ļČĆļź╝ ĒīÉļŗ©ĒĢśĻĖ░ ļ│┤ļŗżļŖö ļŗżņ¢æĒĢ£ ļ╣äņ╣©ņŖĄņĀü ņ×äņāü ņ¦ĢĒøäļź╝ ļ©╝ņĀĆ ĒÖĢņØĖĒĢśĻ│Ā ņØ┤Ēøä ĒĢäņÜöņŗ£ ņ£ä ņ×öļźśļź╝ ĒÖĢņØĖĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓āņØ┤ ļŹö ļ░öļ×īņ¦üĒĢ£ ļ░®ļ▓ĢņØ┤ļØ╝ ĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳Ļ▓Āļŗż.
ĻĘĖ ņÖĖņŚÉļÅä ņ×äņāüĻ▓░Ļ│╝ļĪ£ ĒÅēĻ░ĆļÉ£ ņÖäņĀäņןĻ┤Ćņśüņ¢æ ļÅäļŗ¼ ņŗ£ ņ▓┤ņżæ, ņ▓┤ņżæĒÜīļ│Ąņŗ£ĻĖ░, ņĀĢļ¦źņśüņ¢æĻĖ░Ļ░ä ļ░Å ņĀĢļ¦źņśüņ¢æĻ┤ĆļĀ©Ļ░äņ¦łĒÖś ļ╣łļÅäļÅä ļæÉ ĻĄ░ Ļ░äņŚÉ ņ░©ņØ┤Ļ░Ć ņŚåņŚłļŗż. ņäĀĒ¢ē ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ļōżņŚÉņä£ļÅä ņØ┤ļ¤¼ĒĢ£ ņ¦ĆĒæ£ļōżņØ┤ no-RGRĻĄ░ņŚÉņä£ ņĪ░ĻĖł ļŹö ņóŗĻ▒░ļéś(Riskin et al., 2017) ņ£ĀņØśĒĢ£ ņ░©ņØ┤Ļ░Ć ņŚåļŖö Ļ▓āņ£╝ļĪ£ ļ│┤Ļ│ĀĒĢśĻ│Ā ņ׳ņ¢┤(Torrazza et al., 2015) ļ│Ė ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ņÖĆ ļ╣äņŖĘĒĢ£ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ļź╝ ļ│┤ņśĆļŗż. ļ│Ė ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ņŚÉņä£ ļ╣äļĪØ ĒåĄĻ│äņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņ£ĀņØśĒĢśņ¦ĆļŖö ņĢŖņĢśņ¦Ćļ¦ī ņ┤łĻĘ╣ņåīņĀĆņ▓┤ņżæņČ£ņāØņĢäņØś Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ no-RGRĻĄ░ņØ┤ RGRĻĄ░ņŚÉ ļ╣äĒĢ┤ ņĀĢļ¦źņśüņ¢æĻĖ░Ļ░äņØ┤ 4ņØ╝ ļŹö ņ¦¦Ļ│Ā ņĀĢļ¦źņśüņ¢æĻ┤ĆļĀ©Ļ░äņ¦łĒÖś ļ░£ņāØ ļ╣łļÅäļÅä ļé«ņØĆ Ļ▓āņ£╝ļĪ£ ļéśĒāĆļé¼ļŗż.Torrazza ļō▒(2015)ņØś ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ņŚÉņä£ļÅä ĒåĄĻ│äņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņ£ĀņØśĒĢśņ¦ĆļŖö ņĢŖņĢśņ£╝ļéś no-RGRĻĄ░ņØ┤ ņżæņŗ¼ņĀĢļ¦źĻ┤Ć ņ£Āņ¦ĆĻĖ░Ļ░äņØ┤ 6ņØ╝ ļŹö ņ¦¦ņĢśļŗż. ņĀĢļ¦źņśüņ¢æĻĖ░Ļ░äņØ┤ ĻĖĖņ¢┤ņ¦Ćļ®┤ ņżæņŗ¼ņĀĢļ¦źĻ┤Ć ņé¼ņÜ®ņØ╝ņłś ļśÉĒĢ£ ņ”ØĻ░ĆĒĢśļ®░ ņØ┤ļĪ£ ņØĖĒĢ£ Ļ░ÉņŚ╝, ņĀĢļ¦źņśüņ¢æĻ┤ĆļĀ©Ļ░äņ¦łĒÖś ļō▒ ĒĢ®ļ│æņ”ØņØ┤ ņ”ØĻ░ĆĒĢśĻ▓ī ļÉ£ļŗż(Hermansen & Hermansen, 2005). ņČ£ņāØņ▓┤ņżæņØ┤ ņ×æĻ│Ā ņ×¼Ēā£ĻĖ░Ļ░äņØ┤ ņ¦¦ņØäņłśļĪØ ņןĻ┤Ćņśüņ¢æĻ│ĄĻĖēņØ┤ ņ¢┤ļĀżņÜ┤ ļ¦īĒü╝(Jang, 2011) ņČöĒøä ņ┤łĻĘ╣ņåīņĀĆņ▓┤ņżæ ņČ£ņāØņĢäņØś Ēæ£ļ│Ė ņłśļź╝ ļŖśļĀż ņĪ░ņé¼ĒĢśņŚ¼ ĒåĄĻ│äņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņØśļ»Ė ņ׳ļŖö Ļ▓░Ļ│╝Ļ░Ć ļéśņśżļŖöņ¦Ć ĒÖĢņØĖĒĢ┤ ļ│╝ ĒĢäņÜöĻ░Ć ņ׳ņØä Ļ▓āņ£╝ļĪ£ ļ│┤ņØĖļŗż.
ņØ┤ņāüņŚÉņä£ņÖĆ Ļ░ÖņØ┤ ļ│Ė ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ļŖö ļ»ĖņłÖņĢäņŚÉĻ▓ī ņŻ╝ĻĖ░ņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņ£ä ņ×öļźśļź╝ ĒÖĢņØĖĒĢśņ¦Ć ņĢŖņĢäļÅä ņłśņ£ĀļČłļé┤ņä▒ņØ┤ļéś Ļ┤┤ņé¼ņä▒ ņןņŚ╝ņØś ļ░£ņāØ ļ╣łļÅäļź╝ ļåÆņØ┤ņ¦Ć ņĢŖņØīņØä ņĢī ņłś ņ׳ņŚłņ£╝ļ®░, ļ»ĖņłÖņĢäņØś ņŻ╝ĻĖ░ņĀü ņ£ä ņ×öļźś ĒÖĢņØĖņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ļ╣äĒīÉņĀü ĻĘ╝Ļ▒░ļź╝ ņĀ£ņŗ£ĒĢśļŖö ĻĄŁļé┤ņØś ņ▓½ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ļØ╝ļŖö Ļ▓āņŚÉ ņØśņØśĻ░Ć ņ׳ļŗż. ņŻ╝ĻĖ░ņĀü ņ£ä ņ×öļźś ĒÖĢņØĖņØĆ ĻĘĖ ĻĘ╝Ļ▒░Ļ░Ć ļČĆņĪ▒ĒĢ©ņŚÉļÅä ņłśņ£ĀļČłļé┤ņä▒ ļ░Å Ļ┤┤ņé¼ņä▒ ņןņŚ╝ņØś ņĪ░ĻĖ░ ņ¦ĆĒæ£ļĪ£ ĒĢ┤ņäØļÉśņ¢┤ ņÖöĻĖ░ ļĢīļ¼ĖņŚÉ Ļ┤ĆĒ¢ēņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ Ē¢ēĒĢ┤ņĀĖ ņÖöļŗż. ĻĘĖļ¤¼ļéś ņŻ╝ĻĖ░ņĀü ņ£ä ņ×öļźś ĒÖĢņØĖ ņŗżļ¼┤ļŖö ļ¦ÄņØĆ ņŗ£Ļ░äņØä ĒĢäņÜöļĪ£ ĒĢśļ®░ ĒŚłņÜ® Ļ░ĆļŖźĒĢ£ ņ£ä ņ×öļźśņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ĒĢ®ņØśņĀÉ ņŚåņØ┤ Ļ░äĒśĖņé¼ņØś Ļ▓ĮĒŚś, ņ×äņāüņØśņØś Ļ░£ļ│äņĀüņØĖ ĻĖ░ļīĆ, ņŗĀņāØņĢäņżæĒÖśņ×ÉņŗżņØś ĒöäļĪ£ĒåĀņĮ£ņŚÉ ļö░ļØ╝ ĒÄĖņ░©Ļ░Ć Ēü¼ļŗż(Gregory & Connolly, 2012). ļ│Ė ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ņŚÉņä£ļÅä ļæÉ ĻĄ░ņØś ņÖäņĀäņןĻ┤Ćņśüņ¢æ ļÅäļŗ¼ ņŗ£Ļ░ä Ļ╣īņ¦Ć ņ£ä ņ×öļźś ĒÖĢņØĖ ņØ╝ņłśļź╝ ņĪ░ņé¼ĒĢśņśĆņØä ļĢī ĒĢäņÜöņŗ£ ņ£ä ņ×öļźśļź╝ ĒÖĢņØĖĒĢ£ ĻĄ░ņØś ņ£ä ņ×öļźś ĒÖĢņØĖ ņØ╝ņłśĻ░Ć 4ņØ╝ ņØ┤ņāü Ļ░ÉņåīĒĢ£ Ļ▓āņ£╝ļĪ£ ņĪ░ņé¼ļÉśņŚłļŗż. ļ»ĖņłÖņĢäņŚÉĻ▓ī ņłśņ£Ā ņĀä ļ¦żļ▓ł ņ£ä ņ×öļźśņØś ņ¢æĻ│╝ ņ¢æņāüņØä ĒÖĢņØĖĒĢśņŚ¼ ņØśņé¼ņŚÉĻ▓ī ļ│┤Ļ│ĀĒĢśĻ│Ā ļŗżņØī ņłśņ£ĀņØś ņ¦äĒ¢ēņŚ¼ļČĆļź╝ Ļ▓░ņĀĢĒĢśļŖö ņØ╝ļĀ©ņØś Ļ│╝ņĀĢņØĆ Ļ▓░ņĮö ņĀüņØĆ ļ╣äņÜ®Ļ│╝ ņŗ£Ļ░äņØä ĒĢäņÜöļĪ£ ĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓āņØ┤ ņĢäļŗłļ»ĆļĪ£ 4ņØ╝ ņØ┤ņāüņØś ņ£ä ņ×öļźś ĒÖĢņØĖņØś Ļ░ÉņåīļŖö ņŗżļ¼┤ņØś ĒÜ©ņ£©ņĀü ņĖĪļ®┤ņŚÉņä£ļÅä ņØśļ»ĖĻ░Ć ņ׳ļŗż. Ļ│╝ĒĢÖņĀü ĻĘ╝Ļ▒░Ļ░Ć ļČĆņĪ▒ĒĢ£ ņŻ╝ĻĖ░ņĀü ņ£ä ņ×öļźś ĒÖĢņØĖņØĆ Ļ░äĒśĖ ņŗ£Ļ░ä ļ░Å Ļ▒┤Ļ░ĢĻ┤Ćļ”¼ ļ╣äņÜ®ņØś ņ”ØĻ░Ćļ┐É ņĢäļŗłļØ╝ ĒÖśņ×ÉĻ▓░Ļ│╝ņŚÉ ņśüĒ¢źņØä ļ»Ėņ╣Ā ņłś ņ׳ņ£╝ļ»ĆļĪ£ ņ£ä ņ×öļźśĒÖĢņØĖņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ Ēæ£ņżĆĒÖöļÉ£ ĻĘ╝Ļ▒░ĻĖ░ļ░śņØś ĒöäļĪ£ĒåĀņĮ£ņØ┤ ĒĢäņÜöĒĢśļŗż(Bollineni & Minocha, 2011). ļśÉĒĢ£ ĒöäļĪ£ĒåĀņĮ£ ļ│ĆĻ▓Į ļ░Å ĒÖĢņé░ņØä ņ£äĒĢ┤ņä£ļŖö ĻĄŁļé┤ ņ£ä ņ×öļźś ĒÖĢņØĖ ĒśäĒÖ® ļ░Å ņØśļŻīņ¦äņØś ņØĖņŗØņĪ░ņé¼ļÅä ĒĢäņÜöĒĢĀ Ļ▓āņØ┤ļŗż. ĻĄŁņÖĖņŚÉļŖö ņ£ä ņ×öļźś ĒÖĢņØĖņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ĒśäĒÖ®Ļ│╝ ņØśļŻīņ¦äņØś Ē¢ēņ£ä ļ░Å ņØĖņŗØņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ņĪ░ņé¼ņŚ░ĻĄ¼Ļ░Ć ņ׳ņ£╝ļéś(Bollineni & Minocha, 2011; Gregory & Connolly, 2012) ņĢäņ¦ü ĻĄŁļé┤ņŚÉļŖö ļ│┤Ļ│ĀļÉ£ ļ░öĻ░Ć ņŚåļŗż. ļśÉĒĢ£ ĒĢäņÜöņŗ£ ņ£ä ņ×öļźś ĒÖĢņØĖ ņŗżļ¼┤Ļ░Ć ņŗĀļó░ļÅäņÖĆ ĒāĆļŗ╣ļÅäĻ░Ć ļåÆņØĆ ĻĘ╝Ļ▒░ļĪ£ ĒÖ£ņÜ®ļÉĀ ņłś ņ׳ĻĖ░ ņ£äĒĢ┤ņä£ļŖö ņŻ╝ĻĖ░ņĀü ņ£ä ņ×öļźś ĒÖĢņØĖņØś ņ×Āņ×¼ņĀü ņ£äĒŚśĻ│╝ ĒĢäņÜöņŗ£ ņ£ä ņ×öļźś ĒÖĢņØĖņØś ņØ┤ņĀÉņØä ļ░ØĒ×É ņłś ņ׳ļŖö ļ¼┤ņ×æņ£ä ļīĆņĪ░ĻĄ░ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ļź╝ ĒżĒĢ©ĒĢ£ ņל ņäżĻ│äļÉ£ ļīĆļŗ©ņ£äņØś ļ░śļ│Ą ņŚ░ĻĄ¼Ļ░Ć ĒĢäņÜöĒĢĀ Ļ▓āņ£╝ļĪ£ ņāØĻ░üļÉ£ļŗż.
ļ│Ė ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ņØś ņĀ£ĒĢ£ņĀÉņ£╝ļĪ£ļŖö ļŗ©ņØ╝ĻĖ░Ļ┤ĆņŚÉņä£ņØś ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ļĪ£ ņØ╝ļ░śĒÖöĒĢśļŖöļŹ░ ņ¢┤ļĀżņøĆņØ┤ ņ׳ņ£╝ļ®░ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ļīĆņāüļ│æņøÉņØ┤ ņØ┤ļ»Ė ņŗżļ¼┤ļź╝ ļ│ĆĻ▓ĮĒĢśņŚ¼ ņĀäĒ¢źņĀü ņŚ░ĻĄ¼Ļ░Ć ņ¢┤ļĀżņøĀļŹś ĒĢ£Ļ│äĻ░Ć ņ׳ļŗż. ļ╣äļĪØ ļ│Ė ņŚ░ĻĄ¼Ļ░Ć ļŗ©ņØ╝ĻĖ░Ļ┤ĆņØś ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ņØ┤ĻĖ░ļŖö ĒĢśļéś Ļ┤ĆĒ¢ēņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ Ē¢ēĒĢ┤ņĀĖ ņÖöļŹś ņŻ╝ĻĖ░ņĀü ņ£ä ņ×öļźś ĒÖĢņØĖņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ņ×äņāüĻ▓░Ļ│╝ļź╝ Ļ░ØĻ┤ĆņĀüņØĖ ņ¦ĆĒæ£ļĪ£ ļ│┤ņŚ¼ņżīņ£╝ļĪ£ņŹ© ĻĘĖ ņØ┤ņĀÉņØ┤ ņŚåņØīņØä ĒÖĢņØĖĒĢśņśĆņ£╝ļ®░ ļŗżņ¢æĒĢ£ ņ×äņāüņĀü ņ¦ĢĒøäļź╝ Ļ│ĀļĀżĒĢśņŚ¼ ņןĻ┤Ćņśüņ¢æņØś ņ”Øņ¦ä ļ░Å ņłśņ£ĀļČłļé┤ņä▒Ļ│╝ Ļ┤┤ņé¼ņä▒ ņןņŚ╝ņØś ņ¦ĆĒæ£ļĪ£ ĒÖ£ņÜ®ĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓āņØ┤ ļ»ĖņłÖņĢäņŚÉĻ▓ī ņĀüņĀłĒĢ£ ņśüņ¢æĻ│ĄĻĖēņØä ņ£äĒĢ£ ņĄ£ņĀüņØś ņĀäļץņ×äņØä ņŗ£ņé¼ĒĢ£ļŗż.
ļ│Ė ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ļŖö ņ£äĻ┤Ćņśüņ¢æņØä ĒĢśļŖö ļ»ĖņłÖņĢäņŚÉņä£ ņ£ä ņ×öļźś ĒÖĢņØĖņØś ņ£ĀņÜ®ņä▒ņØä ĒÅēĻ░ĆĒĢśĻĖ░ ņ£äĒĢ┤ ņŻ╝ĻĖ░ņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņ£ä ņ×öļźśļź╝ ĒÖĢņØĖĒĢ£ ļ»ĖņłÖņĢäņÖĆ ĒĢäņÜöņŗ£ ņ£ä ņ×öļźśļź╝ ĒÖĢņØĖĒĢ£ ļ»ĖņłÖņĢäņØś ņ×äņāüĻ▓░Ļ│╝ļź╝ ļ╣äĻĄÉĒĢ£ ĒøäĒ¢źņĀü ņĪ░ņé¼ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ņØ┤ļŗż. ļ│Ė ņŚ░ĻĄ¼Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ ņŻ╝ĻĖ░ņĀü ņ£ä ņ×öļźś ĒÖĢņØĖĻĄ░Ļ│╝ ĒĢäņÜöņŗ£ ņ£ä ņ×öļźś ĒÖĢņØĖĻĄ░ Ļ░ä ņ×äņāüĻ▓░Ļ│╝(ņÖäņĀäņןĻ┤Ćņśüņ¢æ ļÅäļŗ¼ņŗ£Ļ░ä, ņÖäņĀäņןĻ┤Ćņśüņ¢æ ļÅäļŗ¼ ņŗ£ ņ▓┤ņżæ, ņłśņ£ĀļČłļé┤ņä▒ ļ░Å ņ▓┤ņżæĒÜīļ│Ąņŗ£ĻĖ░, ņĀĢļ¦źņśüņ¢æĻĖ░Ļ░ä, ņĀĢļ¦źņśüņ¢æ Ļ┤ĆļĀ©Ļ░äņ¦łĒÖś, Ļ┤┤ņé¼ņä▒ ņןņŚ╝ ļ░£ņāØļ╣łļÅä)ļŖö ĒåĄĻ│äņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņ£ĀņØśĒĢ£ ņ░©ņØ┤Ļ░Ć ņŚåņŚłļŗż. ļö░ļØ╝ņä£ ļ»ĖņłÖņĢäņŚÉĻ▓ī ņłśņ£Āņ¦üņĀä ņŻ╝ĻĖ░ņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņ£ä ņ×öļźśļź╝ ĒÖĢņØĖĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓āņØĆ ĻĘĖ ņØ┤ņĀÉņØ┤ ņŚåņ£╝ļ®░, ņ×äņāüņĀü ņ¦ĢĒøäĻ░Ć ņ׳ļŖö Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ņŚÉļ¦ī ņ£ä ņ×öļźśļź╝ ĒÖĢņØĖĒĢ┤ļÅä ņłśņ£ĀļČłļé┤ņä▒ ļ░Å Ļ┤┤ņé¼ņä▒ ņןņŚ╝ ļ░£ņāØņØä ņ”ØĻ░Ćņŗ£Ēéżņ¦Ć ņĢŖļŖöļŗżļŖö Ļ▓āņØä ĒÖĢņØĖĒĢśņśĆļŗż. ļśÉĒĢ£ ņŻ╝ĻĖ░ņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņ£ä ņ×öļźśļź╝ ĒÖĢņØĖĒĢ©ņ£╝ļĪ£ņŹ© ļ»ĖņłÖņĢäņŚÉĻ▓ī ļ░£ņāØĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ļŖö ņ£ä ņĀÉļ¦ē ņåÉņāüĻ│╝ Ļ░ÖņØĆ ņ×Āņ×¼ņĀüņØĖ ņ£äĒŚśņØä ļ░░ņĀ£ĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳Ļ│Ā, ņØśļŻīĻĖ░Ļ┤ĆņØś ņ×ģņןņŚÉņä£ļŖö ņŗ£Ļ░äĻ│╝ ļ╣äņÜ®ņØä ņĀłĻ░ÉĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ņØä Ļ▓āņØ┤ļŗż.
ļ│Ė ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ļź╝ ĒåĀļīĆļĪ£ ļŗżņØīĻ│╝ Ļ░ÖņØ┤ ņĀ£ņ¢ĖĒĢ£ļŗż. ĻĄŁļé┤ ņŗĀņāØņĢäņżæĒÖśņ×ÉņŗżņØś ņ£ä ņ×öļźś Ļ┤Ćļ”¼ņØś ĒśäĒÖ® ĒīīņĢģ ļ░Å ņ£ä ņ×öļźś ĒÖĢņØĖņØś ņ£ĀņÜ®ņä▒ Ļ▓Ćņ”ØņØä ņ£äĒĢ£ ņל ņäżĻ│äļÉ£ ļ¼┤ņ×æņ£ä ļīĆņĪ░ĻĄ░ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ļź╝ ņĀ£ņ¢ĖĒĢ£ļŗż. ļśÉĒĢ£ Ē¢źĒøä ļ»ĖņłÖņĢäņØś ņןĻ┤Ćņśüņ¢æ ĒĢäņÜöņŗ£ ņ£ä ņ×öļźś ĒÖĢņØĖņ£╝ļĪ£ ņןĻ┤Ćņśüņ¢æņ¦Ćņ╣©ņØ┤ Ļ░£ņäĀļÉśĻ│Ā ĒÖĢņé░ļÉśĻĖ░ļź╝ ņĀ£ņ¢ĖĒĢ£ļŗż.
Figure┬Ā1
RGR: routine evaluation of the gastric residuals, no-RGR: no routine evaluation of the gastric residuals, GR: gastric residuals, FI: feeding intolerance, CBC: complete blood cell count, CRP: C-reactive protein,
*Clinical symptoms of FI: abdomen distension, tense, bruise change in abdominal color, hypoactive of bowel sound, vomiting, large amount of regurgitation, increasing frequency of apnea or bradycardia, positive in stool occult blood test.
Table┬Ā1.
Homogeneity Test of the General and Feeding Characteristics
RGR: routine evaluation of the gastric residuals, no-RGR: no routine evaluation of the gastric residuals, GA: gestational age, LBW: low birth weight, VLBW: very low birth weight, ELBW: extremely low birth weight, RDS: respiratory distress syndrome, BPD: bronchopulmonary dysplasia, PDA: patent ductus arteriosus, IVH: intraventricular hemorrhage, PVL: periventricular leukomalacia, GR: gastric residuals
Table┬Ā2.
Clinical Outcomes for the Evaluation of the RGR
REFERENCES
Abiramalatha, T., Thanigainathan, S. & Balakrishnan, U. (2019). Re-feeding versus discarding gastric residuals to improve growth in preterm infants. Cochrane Database Systemic Review 7, CD012940.
Amendolia, B. (2011). An integrative review of feeding intolerance in preterm infants: State of the science. Clinical Scholars Review, 4(2), 82ŌĆō90.

Ben, X. M. (2008). Nutritional management of newborn infants: Practical guidelines. World Journal of Gastroenterology, 14(40), 6133ŌĆō6139.


Bertino, E., Giuliani, F., Prandi, G., Coscia, A., Martano, C. & Fabris, C. (2009). Necrotizing enterocolitis: Risk factor analysis and role of gastric residuals in very low birth weight infants. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition, 48(4), 437ŌĆō442.


Bollineni, D. & Minocha, A. (2011). Nursing practice of checking gastric residual volumes based on old dogmas: Opportunity to improve patient care while decreasing health care costs. The Journal of the Louisiana State Medical Society, 163(4), 205ŌĆō267.

Cobb, B. A., Carlo, W. A. & Ambalavanan, N. (2004). Gastric residuals and their relationship to necrotizing enterocolitis in very low birth weight infants. Pediatrics, 113(1), 50ŌĆō53.


Duro, D., Mitchell, P. D., Kalish, L. A., Martin, C., McCarthy, M., Jaksic, T. & Duggan, C. (2011). Risk factors for parenteral nutrition-associated liver disease following surgical therapy for necrotizing enterocolitis. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition, 52(5), 595ŌĆō600.



Gokmen, T., Oguz, S., Bozdag, S., Erdeve, O., Uras, N. & Dilmen, U. (2012). A controlled trial of erythromycin and UDCA in premature infants during parenteral nutrition in minimizing feeding intolerance and liver function abnormalities. Journal of Perinatology, 32(2), 123ŌĆō128.



Gregory, K. E. & Connolly, T. C. (2012). Enteral feeding practices in the NICU: Results from a 2009 neonatal enteral feeding survey. Advances in Neonatal Care, 12(1), 46ŌĆō55.


Hans, D. M., Pylipow, M., Long, J. D., Thureen, P. J. & Georgieff, M. K. (2009). Nutritional practices in the neonatal intensive care unit: Analysis of a 2006 neonatal nutrition survey. Pediatrics, 123(1), 51ŌĆō57.


Hay, W. W. (2013). Aggressive nutrition of the preterm infant. Current Pediatrics Reports, 1(4), 229ŌĆō239.


Hermansen, M. C. & Hermansen, M. G. (2005). Intravascular catheter complications in the neonatal intensive care unit. Clinics in Perinatology, 32(1), 141ŌĆō156.


Jang, Y. S. (2011). Nutritional support in premature infants. Hanyang Medical Reviews, 31(4), 246ŌĆō253.

Kaur, A., Kler, N., Saluja, S., Modi, M., Soni, A., Thakur, A. & Garg, P. (2015). Abdominal circumference or gastric residual volume as measure of feed intolerance in VLBW infants. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition, 60(2), 259ŌĆō263.


Lapillonne, A. & Griffin, I. J. (2013). Feeding preterm infants today for later metabolic and cardiovascular outcomes. The Journal of Pediatrics, 162(3 Suppl), S7ŌĆō16.


Li, Y. F., Lin, H. C., Torrazza, R. M., Parker, L., Talaga, E. & Neu, J. (2014). Gastric residual evaluation in preterm neonates: A useful monitoring technique or a hindrance. Pediatrics and Neonatology, 55(5), 335ŌĆō340.


Lucchini, R., Bizzarri, B., Giampietro, S. & De Curtis, M. (2011). Feeding intolerance in preterm infants. How to understand the warning signs. The Journal of Maternal-Fetal & Neonatal Medicine, 24(Suppl 1), 72ŌĆō74.

Mihatsch, W. A., von Schoenaich, P., Fahnenstich, H., Dehne, N., Ebbecke, H., Plath, C. & Pohlandt, F. (2002). The significance of gastric residuals in the early enteral feeding advancement of extremely low birth weight infants. Pediatrics, 109(3), 457ŌĆō459.


Moody, G. J., Schanler, R. J., Lau, C. & Shulman, R. J. (2000). Feeding tolerance in premature infants fed fortified human milk. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition, 30(4), 408ŌĆō412.


Parker, L., Torrazza, R. M., Li, Y., Talaga, E., Shuster, J. & Neu, J. (2015). Aspiration and evaluation of gastric residuals in the neonatal intensive care unit: State of the science. The Journal of Perinatal & Neonatal Nursing, 29(1), 51ŌĆō59.


Pi, S. Y. (2008). Manual of neonatal care. 2nd Eds.Seoul: The Korean Society of Neonatology.
Riskin, A., Cohen, K., Kugelman, A., Toropine, A., Said, W. & Bader, D. (2017). The impact of routine evaluation of gastric residual volumes on the time to achieve full enteral feeding in preterm infants. The Journal of Pediatrics, 189(10), 128ŌĆō134.


Seo, H. Y., Kim, Y. H. & Kim, S. J. (2016). Effects of massage therapy on feeding intolerance and physical growth in premature infants. Child Health Nursing Research, 22(4), 355ŌĆō362.


Shin, J. B. (2009). Enteral feeding for preterm infantsbenefits and risks. Neonatal Medicine, 16(2), 121ŌĆō130.
Sisk, P. M., Lovelady, C. A., Gruber, K. J., Dillard, R. G. & OŌĆÖShea, T. M. (2008). Human milk consumption and full enteral feeding among infants who weigh Ōēż1250 grams. Pediatrics, 121(6), e1528ŌĆō1533.


Torrazza, R. M., Parker, L. A., Li, Y., Talaga, E., Shuster, J. & Neu, J. (2015). The value of routine evaluation of gastric residuals in very low birth weight infants. Journal of Perinatology, 35(1), 57ŌĆō60.



- TOOLS