 |
 |
- Search
| J Korean Crit Care Nurs > Volume 12(3); 2019 > Article |
|
ABSTRACT
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of two single chest physiotherapies mechanically ventilated patients with acute lung injury.
Method
Participants were 30 ICU patients depending entirely on ventilators without self-respiration. Each patients received two single chest physiotherapiesvibration palm cup percussion at hour intervals. Data were analyzed one-way ANOVA and Wilcoxon signed-rank test. Statistical significance was accepted at a p value less than .05.
Results
ibration therapy, dynamic compliance and statics compliance demonstrated a significant increase immediately and remained increased until 30 minutes after chest physiotherapy. palm cum percussion therapy saturation showed a significant increase immediately chest physiotherapyut there were no significant differences in tidal volume, dynamic compliance and statics compliance.
중환자실 입원환자는 응급실이나 병동에서 입원하여 대부분 급성 폐손상(acute lung injury)으로 급격한 호흡부전이 발생하여 인공기도를 삽입하고, 인공호흡기 치료를 받게 된다(Suh, 2006). 급성 폐손상과 인공호흡기치료는 폐포의 가스교환 기능을 저하시키고, 인공기도 자체가 기도의 섬모운동을 방해하고, 기침반사를 억제하여 분비물의 정체를 가져온다(Seo & Kwon, 2009). 이러한 경우에 폐내에 축적된 분비물 제거를 용이하게 하며, 무기폐를 예방하고 폐의 관류와 환기를 증가시키기 위해서는 흉부물리요법의 중재가 필요하다(Baker & Adams, 2002). 흉부물리요법의 주된 목적은 기관분비물의 축적을 예방하고 유동성을 증진하며 산소화의 분산과 효과를 증진시키기 위함이다(Son, 1994; Schans, Postma, Koeter, & Rubin, 1999). 흉부물리요법은 손이나 기계를 사용하여 체외에서 흉곽에 물리적인 힘을 가하여 폐내 분비물의 이동을 돕고 폐내 환기를 증진시키는 것이다(Suh, 2006). 급성 폐손상의 환자는 전반적인 중증도나 급성기의 민감한 폐 상태를 고려하여 객담을 배출시켜야 하므로, 자극은 최소화하고 효과는 최대화 할 수 있는 세심한 흉부물리요법이 필요하다(Jun et al., 2012). 잘못 실시된 흉부물리요법은 과도한 외부자극으로 작용하여 불필요한 산소소모를 일으키고, 혈역동학적 부작용이나 호흡역학적 부작용을 나타낼 수 있기 때문이다(Hamon, Connors, & McCaffree, 1992).
흉부물리요법을 시행할 경우에 일반적으로 체위배액, 흉부타법, 흉부진동 마사지 순으로 하도록 권장하고 있다(Kim, 1995). 두 가지 이상의 흉부물리요법을 함께 병행하는 것이 단독으로 하는 것보다 효과적이라는 것이 일반적인 견해로서 부분적인 요법에 관한 연구들이 다수 있으나 그 방법이 명확히 규명되어 있지는 않다(Jun & Moon, 2000). 현재 임상에서는 대상자의 특성에 맞게 흉부진동 혹은 흉부타진 등으로 과학적 근거없이 습관적으로 시행되는 경우가 대부분이다(Hong & Choi, 2004). 이에 정확한 프로토콜과 과학적 근거에 부합된 효과적인 흉부물리요법에 관한 연구가 이루어져야 될 것이다.
선행연구를 살펴보면, 기존의 연구들은 흉부물리요법의 효과만을 확인하거나 동맥혈가스교환에 미치는 영향을 분석하였지만(Ahn, 1998; Whang & Park, 2000), 인공호흡기를 적용하고 있는 중환자를 대상으로 머리를 내려주는 적극적인 체위배액의 효과나 부작용에 대한 연구는 거의 없는 실정이다. Yoon (1990)은 신경외과 수술 후 환자들에게 진동법과 타진법을 함께 실시하여 객담량은 흉부물리요법을 실시하지 않는 대조군과 차이가 없었으나 동맥혈 산소분압은 대조군에 비해 증가하였음이 확인되었다. Seo와 So (1991)는 의식이 저하된 환자들에게 건강폐하측위와 타진법을 실시한 군과 처치를 전혀 실시하지 않은 대조군 간에 동맥혈 산소분압의 차이가 있었으며, Jun과 Moon (2000)은 의식이 저하된 신경외과 환자에게 진동법과 타진법을 실시한 군과 타진법만 실시한 군을 비교하여 객담량은 차이가 있었으나, 동맥혈 산소분압은 유의한 차이가 없었다고 하였다. Hong과 Choi (2004)는 뇌손상 환자에게 적용한 흉부물리요법의 비교 연구에서 체위변경을 시행한 후 흉부타진법, 수기적, 기계적 흉부진동법을 적용한 결과 기관분비량은 유의한 차이가 있었다. 또한 낭포성 섬유종(cystic fibrosis) 환자들에게 흉부타진과 흉부진동을 추가하여 시행한 군이 그렇지 않은 군에 비해 호흡근의 움직임을 증가하여 호흡기능을 증가한다는 연구가 있다(Marie et al., 2000).
이러한 선행연구에서 흉부물리요법의 효과에 대한 긍정적인 보고가 있지만 과학적 근거는 아직 미비한 실정이며, 흉부물리요법의 효과를 규명할 필요가 있다. 또한 선행연구들은 폐질환은 없고 자가 호흡이 있는 환자들을 대상으로 한 연구들이였다. 이에 본 연구에서는 중환자들을 대상으로 진정제나 무의식으로 자가 호흡이 억제된 상태로 기계호흡을 하는 환자들에게 각각 진동법과 타진법을 실시한 효과를 비교해 보고자 한다.
본 연구는 흉부물리요법이 인공호흡기를 적용한 환자의 산소포화도와 폐환기에 미치는 영향을 알아보기 위한 비동등성 전후비교군 설계의 유사 실험연구 이다.
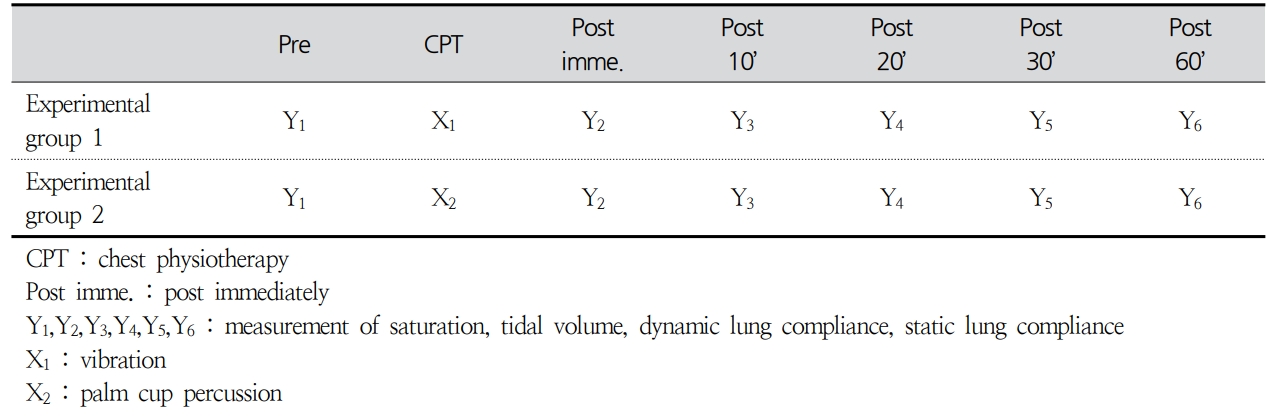
본 연구의 설계는 Figure 1과 같다.
연구대상자는 K도의 S대학병원 내과계 중환자실에 입원하여 인공호흡기 치료를 받는 자로 선정기준은 다음과 같다.
1) 18세 이상인 자
2) 급성 폐손상의 정도가 폐 손상점수(Murray score) 0∼2.5점으로 경증인 자
3) 기관내관(endotracheal tube, tracheostimy tube)를 가지고 있는 자
4) 근이완제나 진정제로 수면을 유도하거나 자발호흡이 없고 servo ventilator에 의존하고 있는 자
5) 사전 동맥혈 산소 분압이 정상 범위 내에 있는 자
6) 흉부타진이나 체위배액이 금기가 아닌 자
7) 연구에 동의한 자(의사소통이 불가능한 경우 보호자가 동의 한 자)
Cohen (1988)에 의한 적절한 대상자수는 효과크기=.04, 검정력= .07, 유의수준= .05에서 15명이었다(Suh, 2006). 따라서 본 연구에서는 제1 실험군(진동법) 15명, 제2 실험군(palm cup 타진법) 15명에게 반복 측정하였다.
내과계 중환자실에 입원하여 인공호흡기 치료를 받는 자로 입실 순서에 맞추어 홀수와 짝수로 나누어 제1실험군(진동법)은 침상 이름표에 빨간색 스티커를 붙이고 제2 실험군(palm cup 타진법)은 침상 이름표에 녹색스티커를 붙여 순차적으로 배정하였다.
본 연구에서의 각 흉부물리요법은 문헌고찰을 통하여 실험적 중재로 시행되었다(American Association of Critical care Nurses, 2003;Kim, 1995). 제1 실험군(진동법), 제2 실험군(palm cup 타진법) 실험 전에 위 내용물의 역류를 방지하기 위하여 위관영양 2시간 뒤에 흉부물리요법을 시행하였다. 외부 자극이나 변동을 가하지 않은 상태에서 각각의 실험군에 흉부물리요법을 시행하기 전에 산소포화도, 일회호흡량, 동적 폐유순도, 정적 폐유순도를 측정하고, 1회 흡인을 시행하였으며, 흉부물리요법 시행 직후, 10분, 20분, 30분, 1시간 동안의 산소포화도, 일회호흡량, 동적 폐유순도, 정적 폐유순도를 측정하였다.
실험의 일관성을 위하여 흉부물리요법의 수행은 연구자와 연구보조원(7년차 간호사)이 시행하였다. 연구보조원에게는 진동법, palm cup 타진법, 흡인의 방법에 대해서 3회 교육하였으며, 연습을 시행하여 연구에 참여할 수 있도록 하였다. 교육 시 연구자가 시범을 보인 후 연구보조원이 수행하는 것을 관찰하고 문제될 수 있는 부분을 서로 지적하여 문제점을 보완해 나갔다.
객담량은 흉부물리요법 시행 전 후 부착된 흡인기와 흡인용기(Ohmeda. USA)를 사용하였으며 흡인은 8∼10초간, 120mmHg의 압력을 유지하면서 2회 반복한 것을 전체 1회로 하였다. 객담량은 2시간 동안 배출된 양을 계측하였으며 흉부물리요법 시행 전과 직후, 폐환기 측정이 끝난 한시간 뒤 30분 간격으로 2회 총 4회 흡인하였다. 2시간 동안 흡인된 분비물량은 전자저울(DAESAN E&T)을 사용하여 계측하였다. 객담량 계측시 흡인하는 동안 카테터 내강의 분비물 제거를 위해 사용된 20cc 생리식염수(31gm) 4개의 무게 124gm과 흡인용기 무게 984gm는 감산하였다.
흉부물리요법 실시 전 후 30초간 MAQUET사에서 제작된 Servo ventilator monitor에 유지되는 대상자의 일회호흡을 기록하였다.
대상자의 산소포화도, 일회호흡량, 동적 폐유순도, 정적 폐유순도를 중재 전 30초 동안 외부 자극이나 변동을 가하지 않은 상태에서 측정하였고 기관내 흡인을 1회 시행하였다.
대상자를 우측위를 취하게 하여 뼈가 돌출된 곳은 피하고 피부 손상을 방지하기 위하여 시트 한장을 등의 폐 좌엽 부위에 대고 대상자가 10회 호흡하는 동안 진동을 적용하였다. 그 후 대상자에게 좌측위를 취하게 한 후 같은 방법으로 진동법을 시행하였다. 진동법 시행 직 후 산소포화도, 일회 호흡량, 동적 폐유순도, 정적 폐유순도를 측정하고 기관내 흡인을 1회 시행하였고 10분, 20분, 30분, 1시간 간격으로 산소포화도, 일회호흡량, 동적 폐유순도, 정적 폐유순도를 측정하였다. 폐환기 측정이 끝난 후 30분 간격으로 2회 흡인을 시행하여 2시간 동안의 객담량을 계측하였다.
대상자를 우측위를 취하게 하여 뼈가 돌출된 곳은 피하여 성인용 palm cup을 잡고 2분간 타격을 가하는 방법으로 등에서 10cm 정도 떨어진 위치에서 손목의 힘을 이용하여 10초 동안 25번의 타격을 가하였다. 그 후 대상자를 좌측위를 취하게 한 후 같은 방법으로 palm cup 타진법을 시행하여 총 4분간 시행하였다. palm cup 타진법 시행 직 후 산소포화도, 일회호흡량, 동적 폐유순도, 정적 폐유순도를 측정하고 기관내 흡인을 1회 시행하였고, 10분, 20분, 30분, 1시간 간격으로 산소포화도, 일회호흡량, 동적 폐유순도, 정적 폐유순도를 측정하였다. 폐환기 측정이 끝난 후 30분 간격으로 2회 흡인을 시행하여 2시간 동안의 객담량을 계측하였다.
두 집단의 일반적 특성에 대한 동질성 검정 결과는 Table 1과 같다.
연구 대상은 제1 실험군(진동법)이 15명, 제2 실험군(palm cup 타진법)이 15명으로 총 30명이었다.
제1 실험군(진동법)에서 성별은 남성 8명(53.3%), 여성 7명(46.7%)이었으며, 연령은 76∼85세가 9명(60.0%)이었고, 연령평균이 74.93±9.52세 였다. 종교는 ‘무’ 10명(66.7%), 최종학력은 초등학교 졸업이 9명(60.0%)으로 높게 나타났고, 진료과는 호흡기 내과가 5명(33.3%)으로 높게 나타났고, 순환기 내과가 4명(26.7%), 소화기 내과가 3명(20.0%)순으로 나타났다. 진단명은 폐렴(both pneumonia)이 4명(26.6%), 폐부종(pulmonary edema)이 2명(13.3%), 만성 폐쇄성 폐질환(COPD)이 1명(6.7%) 순으로 나타났다. 또한 진정제 사용은 ‘유’ 9명(60.0%), ‘무’ 6명(40.0%)이었고, 폐손상 점수(Murray score)는 0.1∼1.0점 6명(40.0%), 1.1∼2.0점 4명(26.6%), 2.1∼2.5점 5명(33.3%)이었다.
제2 실험군(palm cup 타진법)에서 성별은 남성 12명(80.0%), 여성 3명(20.0%)이었으며, 연령은 66∼75세가 6명(40.0%), 76∼85세가 6명(40.0%)이었고, 연령 평균이 72.53±7.615세였다. 종교는 ‘무’ 9명(60.0%), 최종학력은 초등학교 졸업이 7명(46.7%)으로 높게 나타났으며, 진료과는 호흡기 내과가 6명(40.0%)으로 높게 나타났고, 순환기 내과가 3명(20.0%), 신장내과가 3명(20.0%)으로 나타났다. 진단명은 폐렴(both pneumonia)이 4명(26.6%), 폐부종(pulmonary edema)이 2명(13.3%), 폐색전증(both pulmonary thromboembolism)이 1명(6.7%)으로 나타났다. 또한 진정제 사용은 ‘유’ 9명(60.0%), ‘무’ 6명(40.0%)이었고 폐손상 점수(Murray score)는 0.1∼1.0점 5명(33.3%)이었으며, 1.1∼2.0점 10명(66.7%)으로 높게 나타났다.
제1 실험군(진동법)과 제2 실험군(palm cup 타진법)의 일반적 특성으로는 성별, 결혼, 학력, 진료과, 진단명, 수술경험, 인공기도 종류, 진정제 사용 유무, 연령, Murray점수를 조사하였으며, 이는 제1 실험군(진동법)과 제2 실험군(palm cup 타진법) 간에 유의한 차이를 나타내지 않아 두 집단은 동질한 것으로 볼 수 있다(Table 1).
가설 1 : 흉부물리요법의 방법인 진동법과 palm cup 타진법 간에 산소포화도, 일회호흡량, 동적 폐유순도, 정적 폐유순도, 객담량은 차이가 있을 것이다.
산소 포화도, 일회 호흡량, 동적 폐유순도, 정적 폐유순도, 객담량에 유의한 차이가 나타나지 않았다. 따라서 가설 1은 기각되었다(Table 2).
가설 2 : 흉부물리요법의 방법인 진동법은 실시 후 시간 경과에 따라 폐환기에 미치는 효과에 차이가 있을 것이다.
산소 포화도의 경우, 통계적인 유의한 차이를 나타내지 않았으나, 일회 호흡량에서 처치 전 390.73㎖에서 직후에 401.67㎖(p =.035)로 유의한 차이가 있었다. 하지만, 그 이후의 시간경과에 따른 유의한 차이는 나타나지 않았다. 또한, 동적 폐유순도에서도 직후에 30.07 ㎖/cmH2O(p =.014)로 유의한 차이가 나타났으나, 이후의 시간경과에 따른 유의한 차이는 없었다.
정적 폐유순도는 처치 직후에 38.97㎖/cmH2O(p =.002), 10분 후 41.15㎖/cmH2O(p =.003), 20분 후 40.11㎖/cmH2O(p =.004), 30분 후 40.99㎖/cmH2O(p =.004)로 처치 전과의 유의한 차이가 나타났으나, 1시간 경과에 대해서는 38.78㎖/cmH2O(p =.088)으로 유의한 차이가 없었다. 따라서 가설 2는 부분적으로 지지 되었다(Table 3).
가설 3 : 흉부물리요법의 방법인 palm cup 타진법은 실시 후 시간 경과에 따라 폐환기에 미치는 효과에 차이가 있을 것이다.
산소포화도에서 처치 직후에 99.06%(p =.007)으로 유일하게 유의한 결과나 나타났으나, 이후 시간경과에 대한 유의한 차이는 나타나지 않았다. 또한, 일회 호흡량, 동적 폐유순도, 정적 폐유순도에서도 처치 전과 후의 시간경과에 따른 유의한 차이가 나타나지 않았다. 따라서 가설 3은 기각되었다(Table 4).
본 연구는 진정제나 무의식으로 자가 호흡이 억제된 급성 폐손상 환자이면서 인공호흡기를 사용하고 있는 환자에게 진동법, palm cup 타진법을 실시하고 각각의 방법이 산소 포화도, 폐환기, 객담량에 미치는 효과를 비교하여 파악함으로써 임상에서 정규적으로 사용하는 흉부물리요법의 중재방법을 규명하고 근거를 마련하여 임상에 적용하기 위해 시도되었다. 연구결과를 중심으로 논의하고자 한다.
본 연구에서 흉부물리요법의 방법 진동법과 palm cup 타진법 간에 산소포화도, 일회호흡량, 동적 폐유순도, 정적 폐유순도, 객담량에 유의한 차이가 나타나지 않았다. 객담량에서는 제1 실험군(진동법)이 249.87g, palm cup 제2 실험군(palm cup 타진법)이 272.47g으로 약간 많았으나 통계적으로 유의한 차이를 나타내지 않았다. 이는 급성 폐손상 환자를 대상으로 진동법, 손 타진법, palm cup 타진법을 계통적 순번으로 반복측정하여 유의한 차이를 보이지 않았던Suh (2006)의 연구결과와 일치한다.Gallon (1991)의 연구에 의하면 빠른 속도로 타진법을 시행하는 경우가 느린 속도로 타진법을 시행하는 경우보다 기관 분비물의 양이 증가함을 보고하였다. 본 연구에서 객담량에 유의한 차이가 나지 않았던 것은 급성 폐질환 환자들의 폐의 분비물양이 일률적이지 않고 빠른 속도의 지속성을 필요로 하는 좀 더 숙달된 타진법 기술이 부족했던 것으로 생각된다. 또한 본 연구에서는 진동법과 palm cup 타진법을 시행하기 전과 직후에 1회씩 기관내 흡인을 하였고 산소포화도와 폐환기의 측정에 영향을 주지 않기 위해서 측정이 끝난 1시간 뒤에 30분 간격으로 2회 기관내 흡인을 하여 두 시간 동안의 객담량을 계측하여 두군 간에 비교하였다. 객담량이 많은 호흡기 질환자를 대상으로 진동법 군과 palm cup 타진법 군을 각각 단독으로 시행하여 시행 전 후 일정한 시간 간격을 두고 기관내 흡인을 시행하여 각각 흉부물리요법의 사전 사후 결과를 비교함으로써 두군 간의 객담량의 차이를 한번 더 규명해야 될 필요성이 있다고 생각된다.
Jun과 Moon (2000)의 연구에서는 인공기도를 가지고 있고 산소치료를 받고 있는 중환자들을 대상으로 5분간 타진법(제1군), 5분간의 타진법과 10회 호흡운동의 수기진동법(제2군), 5분간의 타진법과 10회 호흡동안의 기계적 진동법(제3군)을 실시한 2시간 동안의 객담량을 비교한 결과 타진법과 수기진동법(제2군)에서 객담량이 5.38㎖로 유의하게 많았다고 보고하였다. 본 연구에서는 제2 실험군(palm cup 타진법)이 약간 많았으나 통계적으로 유의한 차이를 나타내지 못하였다. 이는Jun과 Moon (2000)의 연구 대상자들은 호흡근육이 이완되지 않은 상태이므로 기침을 원활하게 할 수 있어 객담 배출이 용이하였지만, 본 연구에서는 진정제 사용 및 무의식으로 자가 호흡이 억제되어 기침이 불가능하였기 때문이라고 생각된다. 뇌손상으로 의식이 저하된 환자에게 흉부타진(제1군), 흉부타진 후 수기적 흉부진동(제2군), 흉부타진 후 기계적 흉부진동(제3군)을 각각 적용한 후 각 군의 중재 전후 흡인된 분비물량을 비교한Hong과 Choi (2004)의 연구에서는 흉부타진법 후 기계적 흉부진동법(제3군)을 시행한 군이 가장 효과적인 것으로 나타나 본 연구와 차이를 보였다. 이는 흉부물리요법을 단독으로 시행하는 것 보다 환자의 분비물 정체를 예방하기 위해 체위변경을 병행한 흉부물리요법을 시행함으로써 기침을 효과적으로 하지 못하는 환자의 간호중재에 효율적이며 흉부물리요법을 단독으로 시행하는 것 보다 더욱 나은 효과를 나타냄을 알 수 있다.
본 연구에서 진동법을 시행해 처치 전에 비해 시간경과에 따른 폐환기에 미치는 효과를 실험하였으나 산소포화도의 경우 유의한 차이를 나타내지 않았고, 일회호흡량에서 처치 직후에 401.67㎖로 유의한 차이를 보였으나, 그 후의 시간경과에 따른 유의한 차이는 나타나지 않았다. 또한 정적 폐유순도는 처치 후 30분까지는 유의한 차이를 나타내었으나 1시간 경과에 대해서는 유의한 차이를 나타내지 않아 부분적으로 진동법이 효과가 있음을 알 수 있었다. 진동법 시행 직후에 일회호흡량이 증가한 것은 흉부물리요법 직후부터 60분까지 일회호흡량이 증가한 Suh (2006)의 연구와 일치한다. 하지만 본 연구에서는 처치 직후에 증가하여 진동법의 지속성은 규명하기 힘들다. Seo와 Kwon (2009)의 연구에서는 대상자의 특성에 따라 결과변수의 평균이 차이가 남을 보았으며, 65세 이상 연령, 여성, 폐렴이 있는 경우, 흡연을 한 경우 일회호흡량이 줄어든다고 하였다. 본 연구에서 대상자 대부분이 66세에서 85세였으며 폐렴이 26.6%로 많았으며 이러한 요인들이 외생변수로 작용하여 일회호흡량의 측정치에 영향을 주었을 것으로 사료된다.
정적 폐유순도는 30분까지는 유의한 차이를 보였는데 흉부물리요법 시행 후 동적 폐유순도와 정적 폐유순도가 실시 직후에 증가하여 10분까지 유지되었던 Suh (2006)의 연구와 비교할 수 있으나 흉부물리요법의 방법이 손 타진법이라 본 연구와는 차이를 보였다. 또한 정적 폐유순도는 폐와 흉벽의 탄력성을 반영하며, 폐 자체의 문제로 인한 것으로 무기폐나 긴장성 기흉이 발생했거나, 폐 실질 조직내 분비물 정체 시, 급성호흡곤란증후군(ARDS)인 경우 저하된다(Suh, 2006). 따라서 폐압력 변화에 대한 폐용적의 비율은 폐질환의 중증도를 나타낸다고 할 수 있다. 한국산 잡견 14마리를 대상으로 호기말양압(PEEP)에 의한 폐유순도와 산소운반의 변화 및 상관관계를 연구한 Lee 등(1993)의 연구에서 호기말양압의 적용이 산소운반과 총정적 유순도에 영향을 미치는 것으로 나타났으며 급성 폐동맥색전증, 폐부종등에서도 총정적 유순도에 영향을 미치는 것으로 나타났다. 본 연구와는 연구대상과 실험 방법이 다른 연구이나 일정한 호기말양압과 같은 진단명의 호흡기 질 환자를 대상으로 흉부물리요법을 적용한 실험을 시행한 다양한 연구도 필요할 것이라 생각된다.
본 연구에서 palm cup 타진법을 시행하여 시간 경과에 따른 폐환기에 미치는 효과를 실험하였으나, 산소포화도에서 처치직후에 99.06%로 유일하게 증가하여 유의한 결과가 나왔으나 이후 시간경과에 따른 유의한 차이는 나타나지 않았다. 이는 건강한 폐를 하측위로 하여 palm cup 타진법을 시행한 Seo와 Kwon (2009)의 연구에서 산소포화도의 차이가 있는 것으로 나타난 것은 일치하나 중재 직후 감소한 것이 본 연구와 차이가 있었다. 신경외과 환자를 대상으로 흉부타격 및 흉부진동 적용 후 동맥혈 산소분압이 높았다고 한 Yoon (1990)의 연구결과나 건강폐하측위만 한 것보다 측위에서 흉부타진을 병행한 것이 산소분압이 더 높았다고 한 Seo와 So (1991)의 연구결과에서는 산소 분압은 증가하였으나 연구방법의 차이를 보인다. 또한 본 연구에서는 흉부물리요법 시행 후 일회호흡량, 동적 폐유순도와 정적 폐유순도의 시간경과에 따른 유의한 차이가 나타나지 않았으나 Suh (2006)의 연구에서는 일회호흡량이 30분 후에 증가하였고 동적 폐유순도는 직후에 증가하여 20분까지 유지되었고 정적 폐유순도는 직후에 증가하여 본 연구와 차이가 났다. 건강 폐하측위와 흉부타진을 함께 시행한 Seo와 Kwon (2009)의 연구에서 일회호흡량이 다른 중재 방법보다 더 많이 감소하였다. 본 연구에서 palm cup 타진법이 지속적은 아니지만 일시적으로 산소포화도가 증가하였으며 선행연구에서 폐 환기를 증가시키는 효과를 보았다. Jun과 Moon (2000)의 연구에서는 흡인 분비물량의 증가를 최대로 도모하기 위해서는 체위변경과 흉부타법을 포한한 수기적 흉부진동마사지법을 적용하는 것이 가장 효과적이며, 기계적 흉부진동마사지법도 흉부타법만 시행하는 것보다 효과가 높음을 확인하였다. 따라서 palm cup 타진법 단독으로 흉부물리요법을 시행하는 것 보다 체위변경을 병행하여 호흡기 환자들에게 간호중재를 함으로써 폐질환 개선에 도움이 되리라 생각한다.
본 연구에서는 흉부물리요법의 종류 중에 진동법과 palm cup 타진법의 효과를 알기 위해서 각각 개별적으로 시행하였으며 부분적이지만 동적 폐유순도와 정적폐유순도를 증가시키기 위해서 진동법이 palm cup 타진법보다 효과가 있었음을 확인하였으므로 간호사는 임상에서 환자의 활력징후를 모니터링하면서 진동법을 적극 활용한 간호중재를 호흡기 질환 환자에게 제공해야 할 것이다. 또한 진정제 적용 환자나 자발호흡이 없는 환자를 제외한 자발호흡이 있는 환자를 대상으로 선행연구(Jun & Moon, 2000)를 참고하여 체위변경과 다양한 방법의 흉부물리요법을 병행하면서 자발적 기침을 유도한 실험연구도 진행하여 흉부물리요법의 적용 범위를 넓혀가는 것도 중요하리라 생각된다. 또한 임상에서 흔히 사용되고 있는 흉부물리요법의 효과를 명확히 규명함으로써 인공호흡기의 조기이탈과 호흡기 질환 환자의 폐질환 개선에 도움이 되리라 사료된다.
본 연구는 흉부물리요법이 인공호흡기를 적용한 환자의 산소포화도와 폐환기에 미치는 영향을 알아보기 위한 비동등성 전후비교군 설계이다.
인공호흡기를 적용한 환자에게 진동법을 사용한 흉부물리요법을 적용했을 경우 동적 폐유순도는 처치 직후에 증가하였고 정적 폐유순도는 처치 30분까지는 증가했음을 알 수 있다. 하지만 palm cup 타진법에서는 처치 직후에 산소포화도만 증가하였을 뿐 일회호흡량, 동적 폐유순도, 정적 폐유순도는 차이가 없었다.
본 연구에서는 흉부물리요법의 종류 중에 진동법과 palm cup 타진법의 효과를 알기 위해서 각각 개별적으로 시행하였으며 부분적이지만 동적 폐유순도와 정적 폐유순도를 증가시키기 위해서 진동법이 palm cup 타진법보다 효과가 있었음을 확인하였으므로 진동법을 적극 활용한 간호중재를 호흡기 질환 환자에게 제공해야 할 것이다.
따라서 이상의 연구결과를 근거로 다음과 같이 제언한다.
첫째, 진동법과 palm cup 타진법을 병행한 군과 각각 진동법, palm cup 타진법군의 효과를 비교하는 실험 연구를 제언한다. 둘째, 효과적인 흉부물리요법을 검증하기 위해서 일정한 시간 간격을 두고 시행하여 산소포화도, 폐환기의 효과를 반복적으로 추적할 것을 제언한다. 셋째, 진정제나 자발호흡이 없는 환자를 제외한 자발호흡이 있는 환자의 경우 자발적 기침을 유도하여 흉부물리요법을 병행한 실험연구를 제언한다.
Table 1.
Homogeneity Test for General Characteristics (N =30)
| Characteristics | Categories | Experimental group1 (N=15) | Experimental group2 (N=15) | χ2 or t (p) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n (%) | n (%) | |||
| Gender | Male | 8 (53.3) | 12 (80.0) | 2.40 (.121) |
| Female | 7 (46.7) | 3 (20.0) | ||
| Age (years) | 45∼55 | 1 (6.7) | 0 (0.0) | 0.76 (.452) |
| 56∼65 | 1 (6.7) | 3 (20.0) | ||
| 66∼75 | 3 (20.0) | 6 (40.0) | ||
| 76∼85 | 9 (60.0) | 6 (40.0) | ||
| >85 | 1 (6.7) | 0 (0.0) | ||
| Mean±SD | 74.93±9.52 | 72.53±7.62 | ||
| Marital status | Unmarried | 0 (0.0) | 1 (6.7) | 1.03 (.309) |
| Married | 15 (100.0) | 14 (93.3) | ||
| Religion | Yes | 5 (33.3) | 6 (40.0) | 0.14 (.705) |
| No | 10 (66.7) | 9 (60.0) | ||
| Education | Elementary | 9 (60.0) | 7 (46.7) | 2.08 (.720) |
| Middle | 2 (13.3) | 1 (6.7) | ||
| High | 3 (20.0) | 5 (33.3) | ||
| College | 1 (6.7) | 1 (6.7) | ||
| No answer | 0 (0.0) | 1 (6.7) | ||
| Medical department | Infectious medicine | 0 (0.0) | 1 (6.7) | 2.43 (.786) |
| Gastroenterology | 3 (20.0) | 1 (6.7) | ||
| Cardiology | 4 (26.7) | 3 (20.0) | ||
| Renal medicine | 2 (13.3) | 3 (20.0) | ||
| Hematological oncology | 1 (6.7) | 1 (6.7) | ||
| Respiratory medicine | 5 (33.3) | 6 (40.0) | ||
| Diagnosis | Acute kidney injury | 0 (0.0) | 1 (6.7) | 2.43 (.786) |
| Acute myocardial infarction | 1 (6.7) | 0 (0.0) | ||
| Aspiration pneumonia | 1 (6.7) | 2 (13.3) | ||
| Both pneumonia | 4 (26.6) | 4 (26.6) | ||
| Both PTE* | 0 (0.0) | 1 (6.7) | ||
| Pulmonary edema | 2 (13.3) | 2 (13.3) | ||
| Cholecytitis | 1 (6.7) | 0 (0.0) | ||
| Chronic kidney disease | 0 (0.0) | 1 (6.7) | ||
| Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease | 1 (6.7) | 0 (0.0) | ||
| Enteritis sepsis | 1 (6.7) | 0 (0.0) | ||
| Hospital associated pneumonia | 1 (6.7) | 0 (0.0) | ||
| Liver cirrhosis | 1 (6.7) | 0 (0.0) | ||
| Lt pneumonia | 0 (0.0) | 1 (6.7) | ||
| Multiple myeloma | 0 (0.0) | 1 (6.7) | ||
| RLL† pneumonia | 0 (0.0) | 1 (6.7) | ||
| Rt. atelectasis | 1 (6.7) | 0 (0.0) | ||
| Rt. pneumonia | 1 (6.7) | 0 (0.0) | ||
| Septic shock | 0 (0.0) | 1 (6.7) | ||
| Surgical experience | Yes | 11 (73.3) | 10 (66.7) | 0.16 (.690) |
| No | 4 (26.7) | 5 (33.3) | ||
| Tube | Endotracheal tube | 14 (93.3) | 15 (100.0) | 1.03 (.309) |
| Tracheal tube | 1 (6.7) | 0 (0.0) | ||
| Sedative | Yes | 6 (40.0) | 6 (40.0) | 0.00 (1.000) |
| No | 9 (60.0) | 9 (60.0) | ||
| Murray score | 0.1∼1.0 | 6 (40.0) | 5 (33.3) | 1.06 (.297) |
| 1.1∼2.0 | 4 (26.6) | 10 (66.7) | ||
| 2.1∼2.5 | 5 (33.3) | 0 (0.0) | ||
| Mean±SD | 1.57±0.75 | 1.32±0.52 |
Table 2.
Difference of Effects on Ventilation among Two Chest Physiotherapy Methods (N =30)
Table 3.
Effect of the Vibration on Ventilation Over Time
Table 4.
Effect of the Palm Cup Percussion on Ventilation Over Time
REFERENCES
Ahn, Y. M. (1998). The effects of chest vibration prior to endotracheal suctioning on oxygen saturation, heart rate and lung secretions in premature infants. Child Health Nursing Research, 4(2), 245–254.
American Association of Critical care Nurse (2003). AACN procedure manual for critical care (Korean Association of Critical Care Nurses, Trans). Seoul: Kunja Press.
Baker, M. & Adams, S. (2002). An evaluation of a single chest physiotherapy treatment on mechanically ventilated patients with acute lung injury. Physiotherapy Research International, 7(3), 157–169.


Cohen, J. (1988). Statistical power analysis for behavioral science. 2nd Eds. New Jersey: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Gallon, A. (1991). Evaluation of chest percussion in the treatment of patients with copious sputum production. Respiratory Medicine, 85(1), 45–51.


Hammon, W. E., Connors, A. F. & McCaffree, D. R. (1992). Cardiac arrhythmias during postural drainage and chest percussion of critically ill patients. Chest, 102(6), 1836–1841.


Hong, H. S. & Choi, Y. J. (2004). The effect of the chest physiotherapy in brain injury patients. Korean Biological Nursing Science, 6(2), 19–30.
Jun, S. S. & Moon, M. J. (2000). The effect of chest physiotherapy on the amount of tracheal secretion and PaO2. The Korean Journal of Fundamentals of Nursing, 7(3), 355–365.
Jun, S. S., Jeon, J. H., Choi, Y. S., Kim, M. J., Kim, M. H. & Oh, M. Y. (2012). Comparing with high-frequency chest wall oscillation and manual percussion in mechanically ventilated patients. Global Health Nurse, 2(7), 70–81.
Kim, D. S. (1995). Respiratory management of physical. Seoul: Kunja Press.
Lee, S. D., Yoon, S. J., Lee, B. H., Han, S. K., Shim, Y. S., Kim, K. Y. & Han, Y. C. (1993). Relationship of compliance and oxygen transport in experimental acute respiratory failure during positive end-expiratory pressure ventilation. The Korean Academy of Tuberculosis and Respiratory Diseases, 40(1), 6–15.


Williams, M. T., Parsons, D. W., R. Ellis, E., Martin, A. J., Giles, S. E., Frick, R. A. & Grant, R. E. (2000). Energy expenditure during physiotherapistassisted and self-treatment in cystic fibrosis. Physiotherapy Theory and Practice, 16(2), 57–67.

Schans, C. P., Postma, D. S., Koeter, G. H. & Rubin, B. K. (1999). Physiotherapy and bronchial mucus transport. European Respiratory Journal, 13, 1477–1486.


Seo, K. S. & Kwon, E. O. (2009). Chest physical therapy is the patient’s sputum volume ventilation, waste oil purity, effects of tidal volume and oxygen saturation. The Korean Journal of Critical Care Medicine, 2(1), 15–26.
Seo, S. S. & So, H. Y. (1991). Effect of lateral position and chest percussion on pulmonary gas exchange in decreased level of conscious patients. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing, 21(2), 204–217.

Suh, M. H. (2006). Effect of chest physiotherapy on ventilation of mechanically ventilated patients with acute lung injury (Unpublished master’s thesis). Seoul National university, Seoul, Korea.
Son, S. K. (1994). A review of literature and chest physiotherapy for application to nursing. The New medical journal, 37(1), 129–134.
Whang, H. J. & Park, H. J. (2000). The effect of positioning with mechanically ventilatory acute respiratory failure patients on arterial oxygen partial pressure and alveolar-arterial oxygen tension. The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Adult Nursing, 12(2), 234–244.
Yoon, W. S. (1990). Effects of chest percussion and chest vibration on PaO2 and amount of secretion after endotracheal suction (Unpublished master’s thesis). Ewha Womans University, Seoul, Korea.
- TOOLS
-
METRICS

-
- 1 Crossref
- 5,278 View
- 195 Download
- Related articles in J Korean Crit Care Nurs